Osteopontin and thrombospondin-1 play opposite roles in promoting tumor aggressiveness of primary resected non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 27422280
- PMCID: PMC4947364
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2541-5
Osteopontin and thrombospondin-1 play opposite roles in promoting tumor aggressiveness of primary resected non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
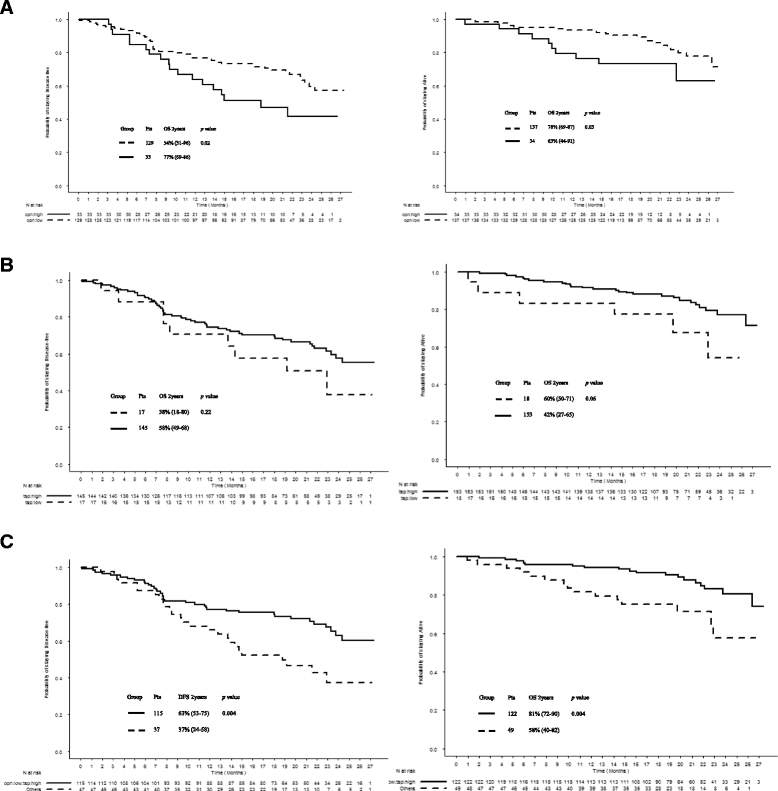
Background: Osteopontin (OPN) and thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) are extracellular matrix proteins secreted by stromal and tumor cells. These proteins appear to have a key role in the tumor microenvironment for cancer development and metastasis. There is little information regarding the prognostic value of the combination of these two proteins in human cancers. Our aim was to clarify clinical significance and prognostic value of each circulating protein and their combination in primary resected non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 171 patients with NSCLC following curative intent surgery from January to December of 2012. Preoperative serums, demographics, clinical and pathological data and molecular profiling were analyzed. Pre-treatment OPN and TSP-1 serum levels were measured by ELISA. Tissue protein expression in primary tumor samples was determined by immunohistochemical analysis.
Results: OPN and TSP-1 serum levels were inversely correlated with survival rates. For each 50 units increment of serum OPN, an increased risk of metastasis by 69 % (unadjusted HR 1.69, 95 % CI 1.12-2.56, p = 0.01) and an increased risk of death by 95 % (unadjusted HR 1.95, 95 % CI 1.15-3.32, p = 0.01) were observed. Conversely, for each 10 units increment in TSP-1, the risk of death was decreased by 85 % (unadjusted HR 0.15, 95 % CI 0.03-0.89; p = 0.04). No statistically significant correlation was found between TSP-1 serum level and distant metastasis-free survival (p = 0.2). On multivariate analysis, OPN and TSP-1 serum levels were independent prognostic factors of overall survival (HR 1.71, 95 % CI 1.04-2.82, p = 0.04 for an increase of 50 ng/mL in OPN; HR 0.18, 95 % CI 0.04-0.87, p = 0.03 for an increase of 10 ng/mL in TSP-1). In addition, the combination of OPN and TSP-1 serum levels remained an independent prognostic factor for overall survival (HR 1.31, 95 % CI 1.03-1.67, p = 0.03 for an increase of 6 ng/mL in OPN/TSP-1 ratio).
Conclusions: Our results show that pre-treatment OPN and TSP-1 serum levels may reflect the aggressiveness of the tumor and might serve as prognostic markers in patients with primary resected NSCLC.
Keywords: Circulating biomarker; Non-small cell lung cancer; Osteopontin; Thrombospondin-1; Tumor microenvironment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prognostic information of serial plasma osteopontin measurement in radiotherapy of non-small-cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2014 Nov 21;14:858. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-858. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25416631 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin is a prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2013 Nov 11;13:540. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-540. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24215488 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic implications of the co-detection of the urokinase plasminogen activator system and osteopontin in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing radiotherapy and correlation with gross tumor volume.Strahlenther Onkol. 2018 Jun;194(6):539-551. doi: 10.1007/s00066-017-1255-1. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Strahlenther Onkol. 2018. PMID: 29340706 English.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of osteopontin expression in patients with prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Biosci Rep. 2021 Aug 27;41(8):BSR20203531. doi: 10.1042/BSR20203531. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33635319 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of STAT3 and phospho-STAT3 expression and survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014 Mar;40(3):311-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2013.11.012. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24332948 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular Dormancy in Cancer: Mechanisms and Potential Targeting Strategies.Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jul;55(3):720-736. doi: 10.4143/crt.2023.468. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 36960624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
THBS1 (thrombospondin-1).Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2020;24(8):291-299. doi: 10.4267/2042/70774. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2020. PMID: 33244322 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin as a Link between Inflammation and Cancer: The Thorax in the Spotlight.Cells. 2019 Aug 2;8(8):815. doi: 10.3390/cells8080815. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31382483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of kininogen 1, osteopontin and α-1-antitrypsin in plasma, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and urine for lung squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis.Oncol Lett. 2020 Apr;19(4):2785-2792. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11376. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32218831 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the ECM in Lung Cancer Dormancy and Outgrowth.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 11;10:1766. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01766. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33014869 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The NSCLC Meta-analyses Collaborative Group. Arriagada R, Auperin A, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy, with or without postoperative radiotherapy, in operable non-small-cell lung cancer: two meta-analyses of individual patient data. Lancet. 2010;375:1267–77. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60059-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

