Human Skeletal Muscle Protein Metabolism Responses to Amino Acid Nutrition
- PMID: 27422520
- PMCID: PMC4942869
- DOI: 10.3945/an.115.011650
Human Skeletal Muscle Protein Metabolism Responses to Amino Acid Nutrition
Abstract
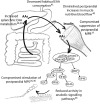
Healthy individuals maintain remarkably constant skeletal muscle mass across much of adult life, suggesting the existence of robust homeostatic mechanisms. Muscle exists in dynamic equilibrium whereby the influx of amino acids (AAs) and the resulting increases in muscle protein synthesis (MPS) associated with the intake of dietary proteins cancel out the efflux of AAs from muscle protein breakdown that occurs between meals. Dysregulated proteostasis is evident with aging, especially beyond the sixth decade of life. Women and men aged 75 y lose muscle mass at a rate of ∼0.7% and 1%/y, respectively (sarcopenia), and lose strength 2- to 5-fold faster (dynapenia) as muscle "quality" decreases. Factors contributing to the disruption of an otherwise robust proteostatic system represent targets for potential therapies that promote healthy aging. Understanding age-related impairments in anabolic responses to AAs and identifying strategies to mitigate these factors constitute major areas of interest. Numerous studies have aimed to identify 1) the influence of distinct protein sources on absorption kinetics and muscle anabolism, 2) the latency and time course of MPS responses to protein/AAs, 3) the impacts of protein/AA intake on muscle microvascular recruitment, and 4) the role of certain AAs (e.g., leucine) as signaling molecules, which are able to trigger anabolic pathways in tissues. This review aims to discuss these 4 issues listed, to provide historical and modern perspectives of AAs as modulators of human skeletal muscle protein metabolism, to describe how advances in stable isotope/mass spectrometric approaches and instrumentation have underpinned these advances, and to highlight relevant differences between young adults and older individuals. Whenever possible, observations are based on human studies, with additional consideration of relevant nonhuman studies.
Keywords: aging; amino acids; leucine; metabolism; muscle.
© 2016 American Society for Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures: WK Mitchell, DJ Wilkinson, BE Phillips, JN Lund, K Smith, and PJ Atherton, no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tischler ME, Desautels M, Goldberg AL. Does leucine, leucyl-tRNA, or some metabolite of leucine regulate protein synthesis and degradation in skeletal and cardiac muscle? J Biol Chem 1982;257:1613–21. - PubMed
-
- Han JM, Jeong SJ, Park MC, Kim G, Kwon NH, Kim HK, Ha SH, Ryu SH, Kim S. Leucyl-tRNA synthetase is an intracellular leucine sensor for the mTORC1-signaling pathway. Cell 2012;149:410–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

