Phosphoproteomics Reveals MAPK Inhibitors Enhance MET- and EGFR-Driven AKT Signaling in KRAS-Mutant Lung Cancer
- PMID: 27422710
- PMCID: PMC5065770
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-15-0506
Phosphoproteomics Reveals MAPK Inhibitors Enhance MET- and EGFR-Driven AKT Signaling in KRAS-Mutant Lung Cancer
Abstract
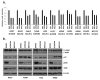
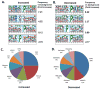
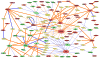
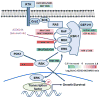
Pathway inhibition of the RAS-driven MAPK pathway using small-molecule kinase inhibitors has been a key focus for treating cancers driven by oncogenic RAS, yet significant clinical responses are lacking. Feedback reactivation of ERK driven by drug-induced RAF activity has been suggested as one of the major drug resistance mechanisms, especially in the context of oncogenic RAS. To determine whether additional adaptive resistance mechanisms may coexist, we characterized global phosphoproteomic changes after MEK inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244) treatment in KRAS-mutant A427 and A549 lung adenocarcinoma cell lines employing mass spectrometry-based phosphoproteomics. We identified 9,075 quantifiable unique phosphosites (corresponding to 3,346 unique phosphoproteins), of which 567 phosphosites were more abundant and 512 phosphosites were less abundant after MEK inhibition. Selumetinib increased phosphorylation of KSR-1, a scaffolding protein required for assembly of MAPK signaling complex, as well as altered phosphorylation of GEF-H1, a novel regulator of KSR-1 and implicated in RAS-driven MAPK activation. Moreover, selumetinib reduced inhibitory serine phosphorylation of MET at Ser985 and potentiated HGF- and EGF-induced AKT phosphorylation. These results were recapitulated by pan-RAF (LY3009120), MEK (GDC0623), and ERK (SCH772984) inhibitors, which are currently under early-phase clinical development against RAS-mutant cancers. Our results highlight the unique adaptive changes in MAPK scaffolding proteins (KSR-1, GEF-H1) and in RTK signaling, leading to enhanced PI3K-AKT signaling when the MAPK pathway is inhibited.
Implications: This study highlights the unique adaptive changes in MAPK scaffolding proteins (KSR-1, GEF-H1) and in RTK signaling, leading to enhanced PI3K/AKT signaling when the MAPK pathway is inhibited. Mol Cancer Res; 14(10); 1019-29. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Defines Feedback Activation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Induced by MEK Inhibition in KRAS-Mutant Lung Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2016 Jul;6(7):754-69. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-1377. Epub 2016 May 6. Cancer Discov. 2016. PMID: 27154822 Free PMC article.
-
Concomitant inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinases and downstream AKT synergistically inhibited growth of KRAS/BRAF mutant colorectal cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 17;8(3):5003-5015. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14009. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28002807 Free PMC article.
-
The PI3K/AKT pathway promotes gefitinib resistance in mutant KRAS lung adenocarcinoma by a deacetylase-dependent mechanism.Int J Cancer. 2014 Jun 1;134(11):2560-71. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28594. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24374738
-
Selumetinib for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017 Aug;26(8):973-984. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2017.1351543. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28675058 Review.
-
Targeting KRAS mutant cancers by preventing signaling transduction in the MAPK pathway.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Feb 5;211:113006. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.113006. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33228976 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of KRAS Concomitant Mutations in Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Sep 29;57(10):1039. doi: 10.3390/medicina57101039. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34684076 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC8 Regulates a Stress Response Pathway in Melanoma to Mediate Escape from BRAF Inhibitor Therapy.Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 1;79(11):2947-2961. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0040. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30987999 Free PMC article.
-
Deoxybouvardin-glucoside induces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting EGFR/MET and AKT signaling pathway.EXCLI J. 2024 Oct 21;23:1287-1302. doi: 10.17179/excli2024-7359. eCollection 2024. EXCLI J. 2024. PMID: 39574967 Free PMC article.
-
RAS: Striking at the Core of the Oncogenic Circuitry.Front Oncol. 2019 Sep 24;9:965. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00965. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31681559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Plasma Metabolite Biomarkers of the MAPK Pathway with MEK Inhibitor RO4987655: Pharmacodynamic and Predictive Potential in Metastatic Melanoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Oct;16(10):2315-2323. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0881. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28637716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roberts PJ, Stinchcombe TE. KRAS mutation: should we test for it, and does it matter? J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:1112–21. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein IB. Cancer Addiction to oncogenes--the Achilles heal of cancer. Science. 2002;297:63–4. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

