Pathology and biology of radiation-induced cardiac disease
- PMID: 27422929
- PMCID: PMC5045085
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrw064
Pathology and biology of radiation-induced cardiac disease
Abstract
Heart disease is the leading global cause of death. The risk for this disease is significantly increased in populations exposed to ionizing radiation, but the mechanisms are not fully elucidated yet. This review aims to gather and discuss the latest data about pathological and biological consequences in the radiation-exposed heart in a comprehensive manner. A better understanding of the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying radiation-induced damage in heart tissue and cardiac vasculature will provide novel targets for therapeutic interventions. These may be valuable for individuals clinically or occupationally exposed to varying doses of ionizing radiation.
Keywords: cardiac disease; endothelial cell; heart; ionizing radiation; myocardium.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japan Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Figures
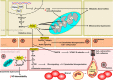
References
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Friday G, et al.. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2007 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 2007;115:e69–171. - PubMed
-
- Cannon B. Cardiovascular disease: biochemistry to behaviour. Nature 2013;493:S2–3. - PubMed
-
- Burns DM. Epidemiology of smoking-induced cardiovascular disease. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2003;46:11–29. - PubMed
-
- Wilson PW, D'Agostino RB, Levy D, et al.. Prediction of coronary heart disease using risk factor categories. Circulation 1998;97:1837–47. - PubMed
-
- Adams J, Palombella VJ, Elliott PJ.. Proteasome inhibition: a new strategy in cancer treatment. Invest New Drugs 2000;18:109–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

