MicroRNA-140 is elevated and mitofusin-1 is downregulated in the right ventricle of the Sugen5416/hypoxia/normoxia model of pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 27422986
- PMCID: PMC7199238
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00264.2016
MicroRNA-140 is elevated and mitofusin-1 is downregulated in the right ventricle of the Sugen5416/hypoxia/normoxia model of pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
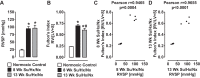
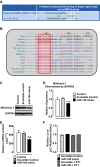
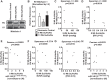
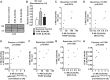
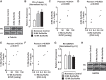
Heart failure, a major cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), is an outcome of complex biochemical processes. In this study, we determined changes in microRNAs (miRs) in the right and left ventricles of normal and PAH rats. Using an unbiased quantitative miR microarray analysis, we found 1) miR-21-5p, miR-31-5 and 3p, miR-140-5 and 3p, miR-208b-3p, miR-221-3p, miR-222-3p, miR-702-3p, and miR-1298 were upregulated (>2-fold; P < 0.05) in the right ventricle (RV) of PAH compared with normal rats; 2) miR-31-5 and 3p, and miR-208b-3p were upregulated (>2-fold; P < 0.05) in the left ventricle plus septum (LV+S) of PAH compared with normal rats; 3) miR-187-5p, miR-208a-3p, and miR-877 were downregulated (>2-fold; P < 0.05) in the RV of PAH compared with normal rats; and 4) no miRs were up- or downregulated with >2-fold in LV+S compared with RV of PAH and normal. Upregulation of miR-140 and miR-31 in the hypertrophic RV was further confirmed by quantitative PCR. Interestingly, compared with control rats, expression of mitofusin-1 (MFN1), a mitochondrial fusion protein that regulates apoptosis, and which is a direct target of miR-140, was reduced in the RV relative to LV+S of PAH rats. We found a correlation between increased miR-140 and decreased MFN1 expression in the hypertrophic RV. Our results also demonstrated that upregulation of miR-140 and downregulation of MFN1 correlated with increased RV systolic pressure and hypertrophy. These results suggest that miR-140 and MFN1 play a role in the pathogenesis of PAH-associated RV dysfunction.
Keywords: heart; heart failure; hypertension; hypertrophy; lungs; miR; pulmonary; rats.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

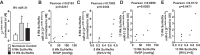
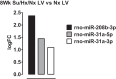
References
-
- Abe K, Toba M, Alzoubi A, Ito M, Fagan KA, Cool CD, Voelkel NF, McMurtry IF, Oka M. Formation of plexiform lesions in experimental severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation : 2747–2754, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Alzoubi A, Toba M, Abe K, O'Neill KD, Rocic P, Fagan KA, McMurtry IF, Oka M. Dehydroepiandrosterone restores right ventricular structure and function in rats with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol : H1708–H1718, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Bogaard HJ, Abe K, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Voelkel NF. The right ventricle under pressure: cellular and molecular mechanisms of right-heart failure in pulmonary hypertension. Chest : 794–804, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Bronicki RA, Baden HP. Pathophysiology of right ventricular failure in pulmonary hypertension. Pediatr Crit Care Med : S15–22, 2010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

