A biphasic effect of TNF-α in regulation of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 27423013
- PMCID: PMC4961303
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.06.004
A biphasic effect of TNF-α in regulation of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in cardiomyocytes
Abstract
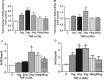
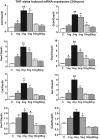
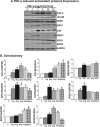
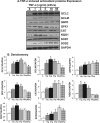
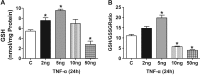
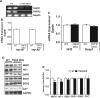
Antagonizing TNF-α signaling attenuates chronic inflammatory disease, but is associated with adverse effects on the cardiovascular system. Therefore the impact of TNF-α on basal control of redox signaling events needs to be understand in more depth. This is particularly important for the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in the heart and in the present study we hypothesized that inhibition of a low level of TNF-α signaling attenuates the TNF-α dependent activation of this cytoprotective pathway. HL-1 cardiomyocytes and TNF receptor1/2 (TNFR1/2) double knockout mice (DKO) were used as experimental models. TNF-α (2-5ng/ml, for 2h) evoked significant nuclear translocation of Nrf2 with increased DNA/promoter binding and transactivation of Nrf2 targets. Additionally, this was associated with a 1.5 fold increase in intracellular glutathione (GSH). Higher concentrations of TNF-α (>10-50ng/ml) were markedly suppressive of the Keap1/Nrf2 response and associated with cardiomyocyte death marked by an increase in cleavage of caspase-3 and PARP. In vivo experiments with TNFR1/2-DKO demonstrates that the expression of Nrf2-regulated proteins (NQO1, HO-1, G6PD) were significantly downregulated in hearts of the DKO when compared to WT mice indicating a weakened antioxidant system under basal conditions. Overall, these results indicate that TNF-α exposure has a bimodal effect on the Keap1/Nrf2 system and while an intense inflammatory activation suppresses expression of antioxidant proteins a low level appears to be protective.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Apoptosis; Nrf2 signaling; Oxidative stress; TNF-α.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Haddad J.J. Antioxidant and prooxidant mechanisms in the regulation of redox(y)-sensitive transcription factors. Cell Signal. 2002;14:879–897. - PubMed
-
- Korashy H.M., El-Kadi A.O. The role of redox-sensitive transcription factors NF-kappaB and AP-1 in the modulation of the Cyp1a1 gene by mercury, lead, and copper. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008;44:795–806. - PubMed
-
- Rahman I., Adcock I.M. Oxidative stress and redox regulation of lung inflammation in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2006;28:219–242. - PubMed
-
- Maillet A., Pervaiz S. Redox regulation of p53, redox effectors regulated by p53: a subtle balance. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012;16:1285–1294. - PubMed
-
- Lee J.M., Li J., Johnson D.A., Stein T.D., Kraft A.D., Calkins M.J., Jakel R.J., Johnson J.A. Nrf2, a multi-organ protector? FASEB J.: Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2005;19:1061–1066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

