A first-in-human phase I study to evaluate the MEK1/2 inhibitor, cobimetinib, administered daily in patients with advanced solid tumors
- PMID: 27424159
- PMCID: PMC6863157
- DOI: 10.1007/s10637-016-0374-3
A first-in-human phase I study to evaluate the MEK1/2 inhibitor, cobimetinib, administered daily in patients with advanced solid tumors
Abstract
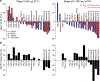
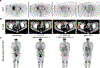
Objective Cobimetinib, a MEK1/2 inhibitor, was administered to patients with advanced solid tumors to assess safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and anti-tumor activity. Methods For dose-escalation, a 3 + 3 design was used. Oral cobimetinib was administered once daily on a 21-day on/7-day off (21/7) or a 14-day on/14-day off (14/14) schedule. Serial plasma samples were collected for pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis on Day 1 and at steady state. In expansion stages, patients with RAS or RAF mutant tumors were treated at the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of the 21/7 or 14/14 schedule. Results Ninety-seven patients received cobimetinib. In the 21/7 dose escalation, 36 patients enrolled in 8 cohorts (0.05 mg/kg-80 mg). Dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) were Grade 4 hepatic encephalopathy, Grade 3 diarrhea, and Grade 3 rash. In the 14/14 dose escalation, 20 patients enrolled in 4 cohorts (60-125 mg). DLTs were Grade 3 rash and Grade 3 blurred vision associated with presence of reversible subretinal fluid. The MTD was 60 mg on 21/7 schedule and 100 mg on 14/14 schedule. Cobimetinib PK showed dose-proportional increases in exposure. The most frequent adverse events attributed to cobimetinib were diarrhea, rash, fatigue, edema, nausea, and vomiting. In patients treated at the 60-mg (21/7) or 100-mg (14/14) dose, one unconfirmed complete response and 6 confirmed partial responses were observed. All responses occurred in melanoma patients; 6 harbored the BRAF(V600E) mutation. Conclusions Cobimetinib is generally well tolerated and durable responses were observed in BRAF(V600E) mutant melanoma patients. Evaluation of cobimetinib in combination with other therapies is ongoing.
Keywords: BRAF; Cobimetinib; MEK inhibitor; Melanoma; Phase I.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

