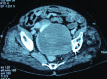
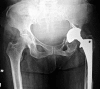
Total hip arthroplasty-related pelvic pseudotumor: Unusual presentation with hydronephrosis
- PMID: 27424805
- PMCID: PMC6197370
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aott.2016.05.001
Total hip arthroplasty-related pelvic pseudotumor: Unusual presentation with hydronephrosis
Keywords: Hip arthroplasty; Pelvic pseudotumor; Polyethylene wear; Urinary retention.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Particle disease osteolysis of the pelvis and the hip after hip arthroplasty.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 May;93(5):453-4. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0b013e3182a92e01. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014. PMID: 24141104 No abstract available.
-
Living history in current orthopaedic hip surgery: intrapelvic teflon granuloma after total hip replacement.Acta Orthop Belg. 2010 Feb;76(1):129-31. Acta Orthop Belg. 2010. PMID: 20306978
-
Pseudotumor Formation in a Metal-on-polyethylene Total Hip Arthroplasty Due to Trunnionosis at the Head-neck Taper.Surg Technol Int. 2015 Nov;27:245-50. Surg Technol Int. 2015. PMID: 26680405
-
Total hip arthroplasty: MR imaging of complications unrelated to metal wear.Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2015 Feb;19(1):31-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1396765. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25633023 Review.
-
Imaging of hip arthroplasty.Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2006 Mar;10(1):30-46. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-934215. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2006. PMID: 16514579 Review.
Cited by
-
Compression of the Rectum, Bladder, and External Iliac Vein Due to Hip Arthroplasty-Related Pseudotumor.Cureus. 2021 Dec 24;13(12):e20671. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20671. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 35106214 Free PMC article.
-
A new strategy to reconstruct type III acetabular bone defect associated with inflammatory pseudotumor: combined medial and lateral acetabular bone grafting: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(50):e8777. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008777. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29390269 Free PMC article.
-
Metallosis following hip arthroplasty: two case reports.J Med Case Rep. 2022 Mar 23;16(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13256-022-03336-4. J Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35317840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paprosky W.G., Perona P.G., Lawrence J.M. Acetabular defect classification and surgical reconstruction in revision arthroplasty. A 6-year follow-up evaluation. J Arthroplast. 1994;9:33–44. - PubMed
-
- Willert H.G., Semlitsch M. Reactions of the articular capsule to wear products of artificial joint prostheses. J Biomed Mater Res. 1977;11:157–164. - PubMed
-
- Boynton E.L., Henry M., Morton J., Waddell J.P. The inflammatory response to particulate wear debris in total hip arthroplasty. Can J Surg. 1995;38:507–515. - PubMed
-
- Kesteris U., Jonsson K., Robertsson O., Onnerfält R., Wingstrand H. Polyethylene wear and synovitis in total hip arthroplasty: a sonographic study of 48 hips. J Arthroplast. 1999;14:138–143. - PubMed
-
- Pandit H., Glyn-Jones S., McLardy-Smith P. Pseudotumours associated with metal-on-metal hip resurfacings. J Bone Jt Surg Br. 2008;90:847–851. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
