Dynamic reconfiguration of the default mode network during narrative comprehension
- PMID: 27424918
- PMCID: PMC4960303
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12141
Dynamic reconfiguration of the default mode network during narrative comprehension
Abstract
Does the default mode network (DMN) reconfigure to encode information about the changing environment? This question has proven difficult, because patterns of functional connectivity reflect a mixture of stimulus-induced neural processes, intrinsic neural processes and non-neuronal noise. Here we introduce inter-subject functional correlation (ISFC), which isolates stimulus-dependent inter-regional correlations between brains exposed to the same stimulus. During fMRI, we had subjects listen to a real-life auditory narrative and to temporally scrambled versions of the narrative. We used ISFC to isolate correlation patterns within the DMN that were locked to the processing of each narrative segment and specific to its meaning within the narrative context. The momentary configurations of DMN ISFC were highly replicable across groups. Moreover, DMN coupling strength predicted memory of narrative segments. Thus, ISFC opens new avenues for linking brain network dynamics to stimulus features and behaviour.
Figures
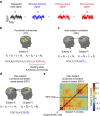
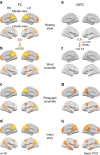
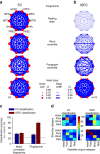
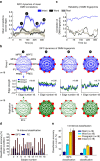

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

