An Autoinhibited Dimeric Form of BAX Regulates the BAX Activation Pathway
- PMID: 27425408
- PMCID: PMC4975667
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.06.010
An Autoinhibited Dimeric Form of BAX Regulates the BAX Activation Pathway
Erratum in
-
An Autoinhibited Dimeric Form of BAX Regulates the BAX Activation Pathway.Mol Cell. 2016 Oct 20;64(2):431. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.10.005. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27768876 No abstract available.
Abstract
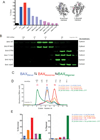
Pro-apoptotic BAX is a cell fate regulator playing an important role in cellular homeostasis and pathological cell death. BAX is predominantly localized in the cytosol, where it has a quiescent monomer conformation. Following a pro-apoptotic trigger, cytosolic BAX is activated and translocates to the mitochondria to initiate mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Here, cellular, biochemical, and structural data unexpectedly demonstrate that cytosolic BAX also has an inactive dimer conformation that regulates its activation. The full-length crystal structure of the inactive BAX dimer revealed an asymmetric interaction consistent with inhibition of the N-terminal conformational change of one protomer and the displacement of the C-terminal helix α9 of the second protomer. This autoinhibited BAX dimer dissociates to BAX monomers before BAX can be activated. Our data support a model whereby the degree of apoptosis induction is regulated by the conformation of cytosolic BAX and identify an unprecedented mechanism of cytosolic BAX inhibition.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Self-regulation of BAX-induced cell death.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 11;7(41):66326-66327. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11948. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27626173 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Acidic domains: "converse readers" for acetylation code.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):80101-80102. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12989. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27806316 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Astrocyte-to-neuron conversion induced by spinal cord injury.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):83831-83832. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13780. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27926495 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

