FoxF1 and FoxF2 transcription factors synergistically promote rhabdomyosarcoma carcinogenesis by repressing transcription of p21Cip1 CDK inhibitor
- PMID: 27425595
- PMCID: PMC5243941
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2016.254
FoxF1 and FoxF2 transcription factors synergistically promote rhabdomyosarcoma carcinogenesis by repressing transcription of p21Cip1 CDK inhibitor
Abstract
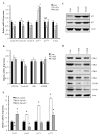
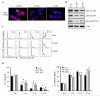
The role of Forkhead Box F1 (FoxF1) transcription factor in carcinogenesis is not well characterized. Depending on tissue and histological type of cancer, FoxF1 has been shown to be either an oncogene or a tumor suppressor. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is the most aggressive pediatric soft-tissue sarcoma. Although FoxF1 is highly expressed in alveolar RMS, the functional role of FoxF1 in RMS is unknown. The present study demonstrates that expression of FoxF1 and its closely related transcription factor FoxF2 are essential for RMS tumor growth. Depletion of FoxF1 or FoxF2 in RMS cells decreased tumor growth in orthotopic mouse models of RMS. The decreased tumorigenesis was associated with reduced tumor cell proliferation. Cell cycle regulatory proteins Cdk2, Cdk4/6, Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E2 were decreased in FoxF1- and FoxF2-deficient RMS tumors. Depletion of either FoxF1 or FoxF2 delayed G1-S cell cycle progression, decreased levels of phosphorylated retinoblastoma protein (Rb) and increased protein levels of the CDK inhibitors, p21Cip1 and p27Kip1. Depletion of both FoxF1 and FoxF2 in tumor cells completely abrogated RMS tumor growth in mice. Overexpression of either FoxF1 or FoxF2 in tumor cells was sufficient to increase tumor growth in orthotopic RMS mouse model. FoxF1 and FoxF2 directly bound to and repressed transcriptional activity of p21Cip1 promoter through -556/-545 bp region, but did not affect p27Kip1 transcription. Knockdown of p21Cip1 restored cell cycle progression in the FoxF1- or FoxF2-deficient tumor cells. Altogether, FoxF1 and FoxF2 promoted RMS tumorigenesis by inducing tumor cell proliferation via transcriptional repression of p21Cip1 gene promoter. Because of the robust oncogenic activity in RMS tumors, FoxF1 and FoxF2 may represent promising targets for anti-tumor therapy.
Figures






Similar articles
-
FOXF1 is required for the oncogenic properties of PAX3-FOXO1 in rhabdomyosarcoma.Oncogene. 2021 Mar;40(12):2182-2199. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01694-9. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33627785 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Expressed FOXF1 Inhibit Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Growth via Inducing Tumor Suppressor and G1-Phase Cell-Cycle Arrest.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 2;21(9):3227. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093227. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32370197 Free PMC article.
-
Methylseleninic acid inhibits microvascular endothelial G1 cell cycle progression and decreases tumor microvessel density.Int J Cancer. 2008 Jan 1;122(1):15-24. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23077. Int J Cancer. 2008. PMID: 17847021
-
Chemopreventive agents alters global gene expression pattern: predicting their mode of action and targets.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2006 Dec;6(8):711-27. doi: 10.2174/156800906779010218. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 17168675 Review.
-
FOXF2 acts as a crucial molecule in tumours and embryonic development.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jun 5;11(6):424. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2604-z. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32503970 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improving anti-tumor efficacy of low-dose Vincristine in rhabdomyosarcoma via the combination therapy with FOXM1 inhibitor RCM1.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 2;13:1112859. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1112859. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36816948 Free PMC article.
-
The FOXM1 Inhibitor RCM-1 Decreases Carcinogenesis and Nuclear β-Catenin.Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Jul;18(7):1217-1229. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0709. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 31040162 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of alveolar macrophages improves the efficacy of endothelial progenitor cell therapy in mouse model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024 Jul 1;327(1):L114-L125. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00274.2023. Epub 2024 May 21. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38772902 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing Allows Generation of the Mouse Lung in a Rat.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Jul 15;210(2):167-177. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202306-0964OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38507610 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of Pulmonary Endothelial Progenitor Cells for Cell-based Therapy Using Interspecies Mouse-Rat Chimeras.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Aug 1;204(3):326-338. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202003-0758OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33705684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Merlino G, Helman LJ. Rhabdomyosarcoma--working out the pathways. Oncogene. 1999;18(38):5340–8. - PubMed
-
- Hayes-Jordan A, Andrassy R. Rhabdomyosarcoma in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2009;21(3):373–8. - PubMed
-
- Breneman JC, Lyden E, Pappo AS, Link MP, Anderson JR, Parham DM, et al. Prognostic factors and clinical outcomes in children and adolescents with metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma--a report from the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study IV. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(1):78–84. - PubMed
-
- Qualman SJ, Morotti RA. Risk assignment in pediatric soft-tissue sarcomas: an evolving molecular classification. Curr Oncol Rep. 2002;4(2):123–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

