Motivational interviewing for the prevention of alcohol misuse in young adults
- PMID: 27426026
- PMCID: PMC6457858
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007025.pub4
Motivational interviewing for the prevention of alcohol misuse in young adults
Abstract
Background: Alcohol use and misuse in young people is a major risk behaviour for mortality and morbidity. Motivational interviewing (MI) is a popular technique for addressing excessive drinking in young adults.
Objectives: To assess the effects of motivational interviewing (MI) interventions for preventing alcohol misuse and alcohol-related problems in young adults.
Search methods: We identified relevant evidence from the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (2015, Issue 12), MEDLINE (January 1966 to July 2015), EMBASE (January 1988 to July 2015), and PsycINFO (1985 to July 2015). We also searched clinical trial registers and handsearched references of topic-related systematic reviews and the included studies.
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials in young adults up to the age of 25 years comparing MIs for prevention of alcohol misuse and alcohol-related problems with no intervention, assessment only or alternative interventions for preventing alcohol misuse and alcohol-related problems.
Data collection and analysis: We used the standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane.
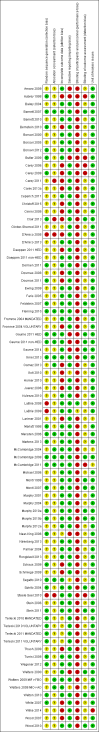
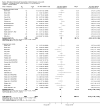
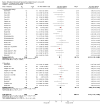
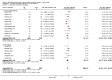
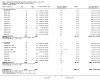
Main results: We included a total of 84 trials (22,872 participants), with 70/84 studies reporting interventions in higher risk individuals or settings. Studies with follow-up periods of at least four months were of more interest in assessing the sustainability of intervention effects and were also less susceptible to short-term reporting or publication bias. Overall, the risk of bias assessment showed that these studies provided moderate or low quality evidence.At four or more months follow-up, we found effects in favour of MI for the quantity of alcohol consumed (standardised mean difference (SMD) -0.11, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.15 to -0.06 or a reduction from 13.7 drinks/week to 12.5 drinks/week; moderate quality evidence); frequency of alcohol consumption (SMD -0.14, 95% CI -0.21 to -0.07 or a reduction in the number of days/week alcohol was consumed from 2.74 days to 2.52 days; moderate quality evidence); and peak blood alcohol concentration, or BAC (SMD -0.12, 95% CI -0.20 to 0.05, or a reduction from 0.144% to 0.131%; moderate quality evidence).We found a marginal effect in favour of MI for alcohol problems (SMD -0.08, 95% CI -0.17 to 0.00 or a reduction in an alcohol problems scale score from 8.91 to 8.18; low quality evidence) and no effects for binge drinking (SMD -0.04, 95% CI -0.09 to 0.02, moderate quality evidence) or for average BAC (SMD -0.05, 95% CI -0.18 to 0.08; moderate quality evidence). We also considered other alcohol-related behavioural outcomes, and at four or more months follow-up, we found no effects on drink-driving (SMD -0.13, 95% CI -0.36 to 0.10; moderate quality of evidence) or other alcohol-related risky behaviour (SMD -0.15, 95% CI -0.31 to 0.01; moderate quality evidence).Further analyses showed that there was no clear relationship between the duration of the MI intervention (in minutes) and effect size. Subgroup analyses revealed no clear subgroup effects for longer-term outcomes (four or more months) for assessment only versus alternative intervention controls; for university/college vs other settings; or for higher risk vs all/low risk participants.None of the studies reported harms related to MI.
Authors' conclusions: The results of this review indicate that there are no substantive, meaningful benefits of MI interventions for preventing alcohol use, misuse or alcohol-related problems. Although we found some statistically significant effects, the effect sizes were too small, given the measurement scales used in the included studies, to be of relevance to policy or practice. Moreover, the statistically significant effects are not consistent for all misuse measures, and the quality of evidence is not strong, implying that any effects could be inflated by risk of bias.
Conflict of interest statement
Oxford Brookes University has received funding from the alcohol industry for prevention programme development and training. There is no perceived conflict of interest between that funding and this Cochrane review.
DF: none known.
LC: none known.
SW: none known.
DA: none known.
NS: none known.
TM: none known.
Figures






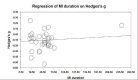

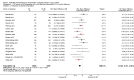





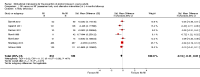















Update of
-
WITHDRAWN: Motivational interviewing for alcohol misuse in young adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 1;(9):CD007025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007025.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 18;7:CD007025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007025.pub4. PMID: 26329400 Updated. No abstract available.
Comment in
-
Reviewing and interpreting the effects of brief alcohol interventions: comment on a Cochrane review about motivational interviewing for young adults.Addiction. 2016 Sep;111(9):1521-7. doi: 10.1111/add.13136. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Addiction. 2016. PMID: 26508301 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Amaro 2009 {published data only}
Aubrey 1998 {unpublished data only}
-
- Aubrey LL. MI with adolescents presenting for outpatient substance abuse treatment. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering. 1998, pp. 1357.
Bailey 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bailey KA, Baker AL, Webster RA, Lewin TJ. Pilot randomized controlled trial of a brief alcohol intervention group for adolescents. Drug and Alcohol Review 2004;23(2):157–66. - PubMed
Barnett 2007 {published data only}
Barnett 2010 {published data only}
Bernstein 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bernstein J, Heeren T, Edward E, Dorfman D, Bliss C, Winter M, et al. A brief motivational interview in a pediatric emergency department, plus 10‐day telephone follow‐up, increases attempts to quit drinking among youth and young adults who screen positive for problematic drinking. Academic Emergency Medicine 2010;17(8):890‐902. - PMC - PubMed
Borsari 2000 {published data only}
-
- Borsari B, Carey KB. Effects of brief motivational interviewing with college student drinkers. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2000;68(4):728‐33. - PubMed
Borsari 2005 {published data only}
Borsari 2012 {published and unpublished data}
Butler 2009 {published data only}
-
- Butler LH, Correia CJ. Brief alcohol intervention with college student drinkers: face‐to‐face versus computerized feedback. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2009;23(1):163‐7. - PubMed
Carey 2006 {published data only}
Carey 2009 {published and unpublished data}
Carey 2011 {published and unpublished data}
Carey 2013a {published data only}
Ceperich 2011 {published data only}
Christoff 2015 {published data only}
-
- Adriana de Oliveira Christoff, Roseli Boerngen‐Lacerda. Reducing substance involvement in college students:A three‐arm parallel‐group randomized controlled trial of a computer‐based intervention. Addictive Behaviors 2015;45:164‐71. - PubMed
Cimini 2009 {published data only}
Clair 2013 {published data only}
Clinton‐Sherrod 2011 {published data only}
-
- Clinton‐Sherrod M, Morgan‐Lopez A, Brown JM, McMillen BA, Cowell A. Incapacitated sexual violence involving alcohol among college women: the impact of a brief drinking intervention. Violence Against Women 2011;17(1):135‐54. - PubMed
D'Amico 2008 {published data only}
-
- D'Amico EJ, Miles JNV, Stern SA, Meredith LS. Brief motivational interviewing for teens at risk of substance use consequences: a randomized pilot study in a primary care clinic. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2008;35(1):53–61. - PubMed
D'Amico 2013 {published data only}
Daeppen 2011 HED {published and unpublished data}
-
- Daeppen JB, Bertholet N, Gaume J, Fortini C, Faouzi M, Gmel G. Efficacy of brief motivational intervention in reducing binge drinking in young men: a randomized controlled trial. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2011;113(1):69‐75. - PubMed
Daeppen 2011 non‐HED {published and unpublished data}
-
- Daeppen JB, Bertholet N, Gaume J, Fortini C, Faouzi M, Gmel G. Efficacy of brief motivational intervention in reducing binge drinking in young men: a randomized controlled trial. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2011;113(1):69‐75. - PubMed
Dermen 2011 {published data only}
Doumas 2008 {published data only}
-
- Doumas DM, Hannah E. Preventing high‐risk drinking in youth in the workplace: a web‐based normative feedback program. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2008;34(3):263–71. - PubMed
Doumas 2011 {published data only}
-
- Doumas DM, Workman C, Smith D, Navarro A. Reducing high‐risk drinking in mandated college students: evaluation of two personalized normative feedback interventions. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2011;40(4):376–85. - PubMed
Ewing 2009 {published data only}
Faris 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Faris AS. Examining process variables in a motivational intervention for college student drinkers. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering 2005;67(7‐B):4102.
Feldstein 2007 {published data only}
-
- Feldstein SW, Forcehimes AA. Motivational Interviewing with underage college drinkers: a preliminary look at the role of empathy and alliance. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 2007;33(5):737‐46. - PubMed
Fleming 2010 {published data only}
Fromme 2004 MANDATED {published data only}
-
- Fromme K, Corbin W. Prevention of heavy drinking and associated negative consequences among mandated and voluntary college students. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2004;72(6):1038‐49. - PubMed
Fromme 2004 VOLUNTARY {published data only}
-
- Fromme K, Corbin W. Prevention of heavy drinking and associated negative consequences among mandated and voluntary college students. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2004;72(6):1038‐49. - PubMed
Gaume 2011 HED {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gaume J, Gmel G, Faouzi M, Bertholet N, Daeppen JB. Is brief motivational intervention effective in reducing alcohol use among young men voluntarily receiving it? A randomized controlled trial. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2011;35(10):1‐9. - PubMed
Gaume 2011 non‐HED {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gaume J, Gmel G, Faouzi M, Bertholet N, Daeppen JB. Is brief motivational intervention effective in reducing alcohol use among young men voluntarily receiving it? A randomized controlled trial. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2011;35(10):1‐9. - PubMed
Gaume 2014 {published data only}
-
- Jacques Gaume, Molly Magill, Richard Longabaugh, Nicolas Bertholet, Gerhard Gmel, andJean‐Bernard Daeppen. Influence of counselor characteristics and behaviors on the efficacy of a brief motivational intervention for heavy drinking in young men — a randomized controlled trial. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2014;38(7):2138‐47. - PubMed
Gmel 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gmel G, Gaume J, Bertholet N, Flückiger J, Daeppen JB. Effectiveness of a brief integrative multiple substance use intervention among young men with and without booster sessions. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2013;44(2):231‐40. - PubMed
Gomez 2013 {unpublished data only}
-
- Gomez CD, Ngantcha M. [Admission aux urgences de Rennes des adolescents enivresse aiguë: Evaluation de l’impact à trois mois d’une intervention motivationnelle auprès des jeunes de 16 à 24 ans admis pour alcoolisation aiguë dans le service d’accueil des urgences de l’Hôpitalde Pontchaillou. Observatoire Français de Drogues et des Toxicomanies, 2013]. www.ofdt.fr/BDD/publications/docs/epfxcdtc.pdf (accessed 15 January 2016); Vol. ].
Goti 2010 {published data only}
-
- Goti J, Diaz R, Serrano L, Gonzalez L, Calvo R, Gual A, Castro J. Brief intervention in substance use among adolescent psychiatric patients: a randomized controlled trial. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2010;19(6):503–11. - PubMed
Horner 2010 {unpublished data only}
-
- Horner KJ. Brief Motivational Interviewing: An Intervention for Alcohol Abusing College Students [unpublished PhD thesis]. State University of New York, 2010.
Juarez 2006 {published data only}
-
- Juarez P, Walters ST, Daugherty M, Radi CA. A randomized trial of motivational interviewing and feedback with heavy drinking college students. Journal of Drug Education 2006;36(3):233‐46. - PubMed
Kulesza 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kulesza M, Apperson M, Larimer M, Copeland A. Brief alcohol intervention for college drinkers: How brief is?. Addictive Behaviors 2010;35(7):730–3. - PubMed
LaBrie 2008 {published data only}
LaBrie 2009 {published data only}
Larimer 2001 {published data only}
-
- Larimer ME, Turner AP, Anderson BK, Foder JS, Kilmer JR, Palmer RS, et al. Evaluating a brief alcohol intervention with fraternities. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2001;62(3):370‐80. - PubMed
Marlatt 1998 {published data only}
-
- Marlatt GA, Baer JS, Kivlahan DR, Dimeff LA, Larimer ME, Quigley LA, et al. Screening and brief intervention for high‐risk college student drinkers results from a 2‐year follow‐up assessment. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1998;66(4):604‐7. - PubMed
Marsden 2006 {published data only}
-
- Marsden J, Stillwell G, Barlow H, Boys A, Taylor C, Hunt N, et al. An evaluation of a brief motivational intervention among young ecstasy and cocaine users: no effect on substance and alcohol use outcomes. Addiction 2006;101(7):1014‐26. - PubMed
Martens 2013 {published data only}
McCambridge 2004 {published data only}
-
- McCambridge J, Strang J. Deterioration over time in effect of Motivational Interviewing in reducing drug consumption and related risk among young people. Addiction 2004;100(4):470‐8. - PubMed
-
- McCambridge J, Strang J. Efficacy of single session MI in reducing drug consumption and perceptions of drug‐related risk and harm among young people: results from a multi‐site cluster randomized trial. Addiction 22004;99(1):39‐52. - PubMed
McCambridge 2008 {published data only}
-
- McCambridge J, Slym R, Strang J. Randomized controlled trial of motivational interviewing compared with drug information and advice for early intervention among young cannabis users. Addiction 2008;103(11):1809–18. - PubMed
McCambridge 2011 {published data only}
-
- McCambridge J, Hunt C, Jenkins R, Strang J. Cluster randomised trial of the effectiveness of motivational interviewing for universal prevention. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2011;114(2):177–84. - PubMed
Michael 2006 {published data only}
-
- Michael KD, Curtin L, Kirkley DE, Jones DL Harris R Jr. Group‐based motivational interviewing for alcohol use among college students: an exploratory study. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice 2006;37(6):629‐34.
Monti 1999 {published data only}
-
- Monti PM, Colby S, Barnett NP, Spirito A, Rohsenow DJ, Myers M, et al. Brief intervention for harm reduction with alcohol‐positive older adolescents in a hospital emergency department. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1999;67(6):989‐94. - PubMed
Monti 2007 {published data only}
-
- Monti P, Barnett NP, Colby SM, Gwaltney CJ, Spirito A, Rohsenow DJ, et al. Motivational interviewing versus feedback only in emergency care for young adult problem drinking. Addiction 2007;102(8):1234–43. - PubMed
Murphy 2001 {published data only}
-
- Murphy JG, Duchnick JJ, Vuchinich RE, Davison JW, Karg R, Olson AM, et al. Relative efficacy of a brief motivational intervention for college student drinkers. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2001;15:373‐9. - PubMed
Murphy 2004 {published data only}
-
- Murphy JG, Benson TA, Vuchinich RE, Deskins MM, Eakin D, Flood AM, et al. A comparison of personalized feedback for college student drinkers delivered with and without a motivational interview. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2004;65(2):200‐3. - PubMed
Murphy 2010a {published data only}
Murphy 2010b {published data only}
Murphy 2012a {published data only}
Naar‐King 2006 {published data only}
-
- Naar‐King S, Lam P, Wang B, Wright K, Parsons JT, Frey MA. Brief report: maintenance of effects of motivational enhancement therapy to improve risk behaviors and HIV‐related health in a randomized controlled trial of youth living with HIV. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2008;33(4):441‐5. - PubMed
-
- Naar‐King S, Wright K, Parsons JT, Frey M, Templin T, Lam P, et al. Healthy choices: motivational enhancement therapy for health risk behaviors in HIV‐positive youth. AIDS Education and Prevention 2006;18(1):1‐11. - PubMed
Nirenberg 2013 {published data only}
Palmer 2004 {unpublished data only}
-
- Palmer RS. Efficacy of the Alcohol Skills Training Program in Mandated and Non‐mandated Heavy Drinking College Students [unpublished PhD thesis]. University of Washington, 2004.
Rongklavit 2013 {published data only}
Schaus 2009 {published data only}
Schmiege 2009 {published data only}
Segatto 2010 {published data only}
-
- Segatto ML, Andreoni S, Souza e Silva R, Diehl A, Pinsky I. Intervenção motivacional breve e brochura educacional em pronto‐socorro para adolescentes e adultos jovens com problemas relacionados ao álcool: um ensaio clínico simples cego randomizado. [Brief motivational interview and educational brochure in emergency room settings for adolescents and young adults with alcohol related problems: a randomized single blind clinical trial]. Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria 2010;33(3):225‐33. - PubMed
Spirito 2004 {published data only}
-
- Spirito A, Monti PM, Barnett NP, Colby SM, Sindelar H, Rohsenow DJ, et al. A randomized clinical trial of a brief motivational intervention for alcohol‐positive adolescents treated in an emergency department. Journal of Pediatrics 2004;145(3):396‐402. - PubMed
Steele Seel 2010 {published data only}
-
- Steele Seel JM. Eliciting Abstinence and Improving Retention in a Vocational and Educational Training Program for Young People: A Pilot Study. Albuquerque, NM: University of New Mexico, 2010.
Stein 2006 {published data only}
Stein 2011 {published data only}
Terlecki 2010 MANDATED {published data only}
-
- Terlecki MA, Larimer ME, Copeland AL. Clinical outcomes of a brief motivational intervention for heavy drinking mandated college students: a pilot study. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 2010;71(1):54‐60. - PubMed
Terlecki 2010 VOLUNTARY {published data only}
-
- Terlecki MA, Larimer ME, Copeland AL. Clinical outcomes of a brief motivational intervention for heavy drinking mandated college students: a pilot study. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 2010;71(1):54‐60. - PubMed
Terlecki 2011 MANDATED {unpublished data only}
-
- Terlecki M. The Long‐term Effect of a Brief Motivational Alcohol Intervention for Heavy Drinking Mandated College Students [PhD thesis]. Baton Rouge, LA: Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, 2010.
Terlecki 2011 VOLUNTARY {published data only}
-
- Terlecki M. The Long‐term Effect of a Brief Motivational Alcohol Intervention for Heavy Drinking Mandated College Students [PhD thesis]. Baton Rouge, LA: Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, 2011.
Thush 2009 {published data only}
Turrisi 2009 {published data only}
Wagener 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wagener TL, Leffingwell TR, Mignogna J, Mignogna MR, Weaver CC, Cooney NJ, et al. Randomized trial comparing computer‐delivered and face‐to‐face personalized feedback interventions for high‐risk drinking among college students. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2012;43:260–7. - PubMed
Walters 2000 {published data only}
-
- Walters ST, Bennett ME, Miller JE. Reducing alcohol use in college students: a controlled trial of two brief interventions. Journal of Drug Education 2000;30(3):361‐72. - PubMed
Walters 2009 MIF v FBO {published data only}
Walters 2009 MIO v AO {published data only}
Walton 2010 {published data only}
White 2007 {published data only}
-
- White HR, Morgan TJ, Pugh LA, Celinska K, Labouvie EW, Pandina RJ. Evaluating two brief substance‐use interventions for mandated college students. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2006;67(2):309‐17. - PubMed
-
- White HR, Mun EY, Pugh L, Morgan TJ. Long‐term effects of brief substance use interventions for mandated college students: sleeper effects of an in‐person personal feedback intervention. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research 2007;31(8):1380‐91. - PubMed
Wilke 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Wilke DJ, Mennicke A, Howell RL, Magnuson AB. A peer‐facilitated intervention to reduce risky drinking among fraternity and sorority members. Journal of Social Work Practice in the Addictions 2014;14(1):42‐63.
Wood 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wood MD, Capone C, Laforge R, Erickson DJ, Brand NH. Brief motivational intervention and alcohol expectancy challenge with heavy drinking college students: a randomized factorial study. Addictive Behaviors 2007;32(11):2509–28. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Baer 1992 {published data only}
-
- Baer JS, Marlatt GA, Kivlahan DR, Fromme K, Larimer ME, Williams E. An experimental test of three methods of alcohol risk reduction with adults. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1992;60(6):974‐9. - PubMed
Battjes 2004 {published data only}
-
- Battjes RJ, Gordon MS, O'Grady KE, Kinlock TW, Katz EC, Sears EA. Evaluation of a group‐based substance abuse treatment program for adolescents. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2004;27(2):123‐34. - PubMed
Carey 2013b {published data only}
Collins 2002 {published data only}
-
- Collins SE, Carey KB, Sliwinski MJ. Mailed personalized normative feedback as a brief intervention for at‐risk college drinkers. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2002;63(5):559‐67. - PubMed
Cowell 2012 {published data only}
Dauer 2005 {published data only}
-
- Dauer ARM, Rubio ES, Coris ME, Valls JM. Brief Intervention in alcohol‐positive traffic casualties: is it worth the effort?. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2006;41(1):76‐83. - PubMed
Gregory 2001 {unpublished data only}
-
- Gregory BM. College Alcohol and Life Skills Study with Student‐Athletes [unpublished PhD thesis abstract: 2001‐95013‐033] 2001.
Hayes 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- Hayes, BB. Comparing the effectiveness of cognitive‐behavioral group therapy with and without motivational interviewing at reducing the social anxiety, alcohol consumption, and negative consequences of socially anxious college students. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering 67(9‐B):5405.
Hustad 2014 {published data only}
Kypri 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kypri K, Langley JD, Saunders JB, Cashell‐Smith ML, Herbison P. Randomized controlled trial of web‐based alcohol screening and brief intervention in primary care. Archives of Internal Medicine 2008;168(5):530‐6. - PubMed
Kypri 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kypri K, Hallett J, Howat P, McManus A, Maycock B, Bowe S, et al. Randomized controlled trial of proactive web‐based alcohol screening and brief intervention for university students. Archives of Internal Medicine 2009;169(16):1508‐14. - PubMed
LaBrie 2002 {published data only}
-
- LaBrie JW. Weighing the pros and cons: A brief motivational intervention reduces risk associated with drinking and unsafe sex. Dissertation Abstracts International 2002.
LaBrie 2011 {published data only}
Longabaugh 2001 {published data only}
-
- Longabaugh R, Woolard RE, Nirenberg TD, Minugh AP, Becker B, Clifford PR, et al. Evaluating the effects of a brief motivational intervention for injured drinkers in the emergency department. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2001;62(6):806‐16. - PubMed
Magill 2009 {published data only}
Maisto 2001 {published data only}
-
- Maisto SA, Conigliaro J, McNeil M, Kraemer K, Conigliaro RL, Kelley ME. Effects of two types of brief intervention and readiness to change on alcohol use in hazardous drinkers. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2001;62(5):605‐14. - PubMed
Morgenstern 2007 {published data only}
-
- Morgenstern J, Irwin TW, Wainberg ML, Parsons JT, Muench F, Bux DA Jr, et al. A randomized controlled trial of goal choice interventions for alcohol use disorders among men who have sex with men. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2007;75(1):72‐84. - PubMed
Morgenstern 2012 {published data only}
Murphy 2012b {published data only}
Nirenberg 2013b {published data only}
Ondersma 2007 {published data only}
Peterson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Peterson PL, Baer JS, Wells EA, Ginzler JA, Garrett SB. Short‐term effects of a brief motivational intervention to reduce alcohol and drug risk among homeless adolescents. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2006;20(3):254‐64. - PubMed
Potts 2001 {unpublished data only}
-
- Potts KAF. Efficacy of the Alcohol Skills Training Program, a Brief Group Intervention for High Risk College Student Drinkers [unpublished PhD thesis]. Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska, 2001.
Smith 2003 {published data only}
-
- Smith AJ, Hodgson RJ, Bidgeman K, Sheherd JP. A randomized controlled trial of a brief intervention after alcohol‐related facial injury. Addiction 2003;98(1):43‐52. - PubMed
Spirito 2011 {published data only}
-
- Spirito A, Sindelar‐Manning H, Colby SM, Barnett NP, Lewander W, Rosenhow DJ, et al. Individual and family motivational interventions for alcohol‐positive adolescents treated in an emergency department: results of a randomized clinical trial. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 2011;165(3):269‐74. - PMC - PubMed
Wei Sun 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sun W, Skara S, Sun P, Dent CW, Sussman S. Project towards no drug abuse: long‐term substance use outcomes evaluation. Preventive Medicine 2006;42(3):188‐92. - PubMed
Woodhall 2007 {published data only}
-
- Woodhall WG, Delaney HD, Kunitz SJ, Westerberg VS, Zhao H. A randomized trial of a DWI Intervention program for first offenders: intervention outcomes and interactions with antisocial personality disorder among a primarily American‐Indian sample. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2007;31(6):974‐87. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Cunningham 2015 {published data only}
ISRCTN31234060 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN31234060. Brief motivational intervention in adolescents treated in emergency departments for acute alcohol intoxication: a randomized controlled trial. http://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN31234060 (accessed 1 April 2016). - PMC - PubMed
NCT00229983 {published data only}
-
- NCT00229983. Medical office intervention for adolescent drug use. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00229983 (accessed 1 April 2016).
NCT00907309 {published data only}
-
- NCT00907309. Dental and medical office iMET to reduce teen tobacco, alcohol, and drug use. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00907309 (accessed 1 April 2016).
NCT01128140 {published data only}
-
- NCT01128140. Efficacy trial of warrior check‐up. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01128140 (accessed 1 April 2016).
NCT01204229 {published data only}
-
- NCT01204229. Motivational and cognitive intervention for college drinkers (MCID). https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01204229 (accessed 1 April 2016).
NCT01546025 {published data only}
-
- NCT01546025. Brief alcohol intervention for school‐to‐work transitions. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01546025 (accessed 1 April 2016).
NCT01616212 {published data only}
-
- NCT01616212. Early intervention for minors in possession of alcohol/drugs: a feasibility study (MAST1). https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01616212 (accessed 1 April 2016).
NCT02056535 {published data only}
-
- NCT02056535. Screening and brief intervention in the ED among Mexican‐origin young adults. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02056535 (accessed 1 April 2016).
NCT02252471 {published data only}
-
- NCT02252471. Choices‐teen: a bundled risk reduction intervention for juvenile justice females. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02252471 (accessed 1 April 2016).
Newbury‐Birch 2014 {published data only}
-
- Newbury‐Birch D, Scott S, O’Donnell A, Coulton S, Howel D, McColl E, et al. A pilot feasibility cluster randomised controlled trial of screening and brief alcohol intervention to prevent hazardous drinking in young people aged 14–15 years in a high school setting (SIPS JR‐HIGH). Public Health Research. NIHR Journals Library 2014;No. 2.6:Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK263999/. [DOI: 10.3310/phr02060] - DOI - PubMed
Walton 2012 {published data only}
-
- Walton MA, Bohnert K, Resko S, Barry KL, Chermack ST, Zucker RA, et al. Computer and therapist based brief interventions among cannabis‐using adolescents presenting to primary care: one year outcomes. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2013;132(3):646‐53. [DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2013.04.020] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
ACTRN12613000108718 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12613000108718. Brief telephone delivered personality‐targeted versus standard motivational interviewing for for reducing future alcohol use and related harm in young people accessing emergency departments. https://www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?ACTRN=1261... (accessed 1 April 2016).
Additional references
Bandura 1977
-
- Bandura A. Social Learning Theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1977.
Bertholet 2014
Burke 2002a
-
- Burke BL, Vassilev G, Kantchelov A, Zweben A. Motivational interviewing with couples. Motivational Interviewing: Preparing People for Change. 2nd Edition. New York: Guilford Press, 2002:347‐61.
Burke 2002b
-
- Burke B, Arkowitz H, Dunn C. The efficacy of motivational interviewing. In: W.R. Miller, S. Rollnick editor(s). Motivational interviewing: Preparing People for Change. 2nd Edition. New York: Guilford Press, 2002:217‐50.
Burke 2003
-
- Burke BL, Arkowitz H, Menchola M. The efficacy of motivational interviewing: a meta‐analysis of controlled clinical trials. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2003;71(5):843‐61. - PubMed
Carey 2007
Collins1985
-
- Collins RL, Parks GA, Marlatt GA. Social determinants of alcohol consumption: The effects of social interaction and model status on the self‐administration of alcohol. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1985;53(2):189‐200. - PubMed
CONSORT 2010
-
- CONSORT. Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials. Library for health research reporting. http://www.equator‐network.org/resource‐centre/library‐of‐health‐research‐reporting/ (accessed 16 July 2010).
Corrao 1999
-
- Corrao G, Bagnardi V, Zambon A, Arico S. Exploring the dose‐response relationship between alcohol consumption and the risk of several alcohol‐related conditions: a meta‐analysis. Addiction 1999;94(10):1551‐73. - PubMed
Dunn 2001
-
- Dunn C, Deroo L, Rivara FP. The use of brief interventions adapted from motivational interviewing across behavioral domains: a systematic review. Addiction 2001;96(12):1725‐42. - PubMed
Edwards 1994
-
- Edwards AP, Babor G, Casswell TF, Ferrence S. The individual's drinking and degree of risk. Alcohol Policy and the Public Good. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1994.
Fewtrell 2008
-
- Fewtrell MS, Kennedy K, Singhal A, Martin RM, Ness A, Hadders‐Algra M, et al. How much loss to follow‐up is acceptable in long‐term randomised trials and prospective studies?. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2008;93(6):458‐61. - PubMed
Foxcroft 2014
-
- Foxcroft DR. Can prevention classification be improved by considering the function of prevention?. Prevention Science 2014;15(6):818‐22. - PubMed
Foxcroft 2015
GRADE 2004
Grant 2015
Greenfield 2001
-
- Greenfield TK. Individual risk of alcohol related disease and problems. In: Heather N, Stockwell T editor(s). International Handbook of Alcohol Dependence and Problems. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, 2001:413‐438.
Grenard 2006
-
- Grenard JL, Ames SL, Pentz MA, Sussman S. Motivational interviewing with adolescents and young adults for drug‐related problems. Int J Adolesc Med Health 2006;18(1):53‐67. - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines 1. Introduction‐GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383‐94. - PubMed
Hettema 2005
-
- Hettema J, Steele J, Miller WR. Motivational Interviewing. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology 2005;1:91‐111. - PubMed
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
Hrobjartsson 2014
Huh 2015
Kohler 2015
-
- Kohler S, Hofmann A. Can motivational interviewing in emergency care reduce alcohol consumption in young people? A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2015;50(2):107‐17. - PubMed
Larimer 2007
-
- Larimer ME, Cronce JM. Identification, prevention, and treatment revisited: individual‐focused college drinking prevention strategies 1999–2006. Addictive Behaviors 2007;32(11):2439–68. - PubMed
Lundahl 2010
-
- Lundahl BW, Kunz C, Brownell C, Tollefson D, Burke BL. A meta‐analysis of motivational interviewing: twenty‐five years of empirical studies. Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE): Quality‐assessed Reviews. 2010;20(2):137‐60.
Maisto 1999
-
- Maisto SA, Carey KB, Bradizza CM. Social learning theory. In: Blane HT, Leonard KE editor(s). Psychological Theories of Drinking and Alcoholism. 2nd Edition. New York: Guilford Press, 1999:106‐163.
Miller 1983
-
- Miller WR. Motivational interviewing with problem drinkers. Behavioral Psychotherapy 1983;11(2):147‐72.
Miller 1993
-
- Miller WR, Benefield RG, Tonigan JS. Enhancing motivation for change in problem drinking; a controlled comparison of two therapist styles. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1993;61:455‐61. - PubMed
Miller 1995a
-
- Miller WR, Rollnick S. What is motivational interviewing?. Behavioral and Cognitive Psychotherapy 1995;23(4):325–34. - PubMed
Miller 1995b
-
- Miller WR, Tonigan JS, Longabaugh R. The Drinker Inventoryof Consequences (DrInC): An Instrument for Accessing Adverse Consequences of Alcohol Abuse (Test Manual). NIAAA Project MATCH Monograph Series, NIH Publication No. 95‐3911. Vol. 4, Bethesda, MD: National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, 1995.
Miller 1996
-
- Miller WR. Motivational interviewing: research, practice, and puzzles. Addictive Behaviors 1996;21:835‐42. - PubMed
Miller 2002
-
- Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational Interviewing: Preparing People to Change Addictive Behavior. New York: Guilford Press, 2002.
Mun 2015
Noonan 1997
-
- Noonan WC, Myers TB. Motivational interviewing: a review. Journal of Substance Misuse 1997;2:8‐16.
O' Leary 2004
-
- O' Leary TT, Monti PM. Motivational enhancement and other brief interventions for adolescent substance abuse: foundations, applications and evaluations. Addiction 2004;99(Suppl 2):63‐75. - PubMed
Paterson 1985
-
- Paterson GA, Forgatch MS. Therapist behavior as a determinant for client non compliance: a paradox for the behavior modifier. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1985;53:846‐51. - PubMed
Petrosino 2005
-
- Petrosino A, Soydan H. The impact of program developers as evaluators on criminal recidivism: results from meta‐analyses of experimental and quasi‐experimental research. Journal of Experimental Criminology 2005;1(4):435‐50.
Prochaska 1992
-
- Prochaska JO, DiClemente CC, Norcross JC. In search of how people change: applications to addictive behaviors. American Psychologist 1992;47:1102‐14. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rubak 2006
Saunders 1993
-
- Saunders JB, Aasland OG, Babor TF, Delafuente JR, Grant M. Development of the Alcohol‐Use Disorders IdentificationTest (AUDIT): WHO collaborative project on early detection of persons with harmful alcohol consumption. Addiction 1993;88(6):791–804. - PubMed
Smedslund 2011
Sobell 1992
-
- Sobell LC, Sobell MB. Timeline follow‐back: technique for assessing self‐reported alcohol consumption. In: Litten RZ, Allen JP editor(s). Measuring Alcohol Consumption: Psychosocial and Biological Methods. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 1992:41‐72.
Tait 2003
-
- Tait RJ, Hulse GK. A systematic review of the effectiveness of brief interventions with substance using adolescents by type of drug. Drug and Alcohol Review 2003;22(3):337–46. - PubMed
Tanner‐Smith 2015
Thakker 1998
-
- Thakker KD. An overview of health risks and benefits of alcohol consumption. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 1998;22(7 Suppl):285‐98. - PubMed
Vasilaki 2006
-
- Vasilaki EI, Hosier SG, Cox WM. The efficacy of motivational interviewing as a brief intervention for excessive drinking: a meta‐analytic review. Alcohol Alcohol 2006;41(3):328‐35. - PubMed
White 1989
-
- White HR, Labouvie EW. Towards the assessment of adolescent problem drinking. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 1989;50(1):30‐7. - PubMed
WHO 2011
-
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health. Geneva: WHO, 2011.
WHO 2014
-
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2014. Geneva: WHO, 2014.
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

