Hypoglycaemia when adding sulphonylurea to metformin: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 27426428
- PMCID: PMC5061791
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13059
Hypoglycaemia when adding sulphonylurea to metformin: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Aims: The risk of hypoglycaemia may differ among sulphonylureas (SUs), but evidence from head-to-head comparisons is sparse. Performing a network meta-analysis to use indirect evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs), we compared the relative risk of hypoglycaemia with newer generation SUs when added to metformin.
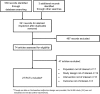
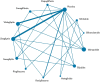
Methods: A systematic review identified RCTs lasting 12-52 weeks and evaluating SUs added to inadequate metformin monotherapy (≥1000 mg/day) in type 2 diabetes. Adding RCTs investigating the active comparators from the identified SU trials, we established a coherent network. Hypoglycaemia of any severity was the primary end point.
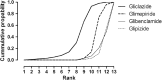
Results: Thirteen trials of SUs and 14 of oral non-SU antihyperglycaemic agents (16 260 patients) were included. All reported hypoglycaemia only as adverse events. Producing comparable reductions in HbA1C of -0.66 to -0.84% (-7 to -9 mmol/mol), the risk of hypoglycaemia was lowest with gliclazide compared to glipizide (OR 0.22, CrI: 0.05 to 0.96), glimepiride (OR 0.40, CrI: 0.13 to 1.27), and glibenclamide (OR 0.21, CrI: 0.03 to 1.48). A major limitation is varying definitions of hypoglycaemia across studies.
Conclusions: When added to metformin, gliclazide was associated with the lowest risk of hypoglycaemia between the newer generation SUs. Clinicians should consider the risk of hypoglycaemia agent-specific when selecting an SU agent.
Keywords: hypoglycaemia; network meta-analysis; oral antiglycaemic agents; relative safety; sulphonylurea; type 2 diabetes.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient‐centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015; 38: 140–149. - PubMed
-
- Rendell M. The role of sulphonylureas in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 2004; 64: 1339–1358. - PubMed
-
- Simon D, de Pablos‐Velasco P, Parhofer KG, Gonder‐Frederick L, Duprat Lomon I, Vandenberghe H, et al. Hypoglycaemic episodes in patients with type 2 diabetes – risk factors and associations with patient‐reported outcomes: the PANORAMA study. Diabetes Metab 2015; 41: 470–479. - PubMed
-
- Liu SC, Tu YK, Chien MN, Chien KL. Effect of antidiabetic agents added to metformin on glycaemic control, hypoglycaemia and weight change in patients with type 2 diabetes: a network meta‐analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 2012; 14: 810–820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

