The effects of orally administered Bacillus coagulans and inulin on prevention and progression of rheumatoid arthritis in rats
- PMID: 27427194
- PMCID: PMC4947834
- DOI: 10.3402/fnr.v60.30876
The effects of orally administered Bacillus coagulans and inulin on prevention and progression of rheumatoid arthritis in rats
Abstract
Background: Probiotics have been considered as an approach to addressing the consequences of different inflammatory disorders. The spore-forming probiotic strain Bacillus coagulans has demonstrated anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating effects in both animals and humans. The prebiotic inulin also potentially affects the immune system as a result of the change in the composition or fermentation profile of the gastrointestinal microbiota.
Objective: In the present study, an in vivo model was conducted to investigate the possible influences of probiotic B. coagulans and prebiotic inulin, both in combination and/or separately, on the downregulation of immune responses and the progression of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), using arthritis-induced rat model.
Design: Forty-eight healthy male Wistar rats were randomly categorized into six experimental groups as follows: 1) control: normal healthy rats fed with standard diet, 2) disease control (RA): arthritis-induced rats fed with standard diet, 3) prebiotic (PRE): RA+ 5% w/w long-chain inulin, 4) probiotic (PRO): RA+ 10(9) spores/day B. coagulans by orogastric gavage, 5) synbiotic (SYN): RA+ 5% w/w long-chain inulin and 10(9) spores/day B. coagulans, and 6) treatment control: (INDO): RA+ 3 mg/kg/day indomethacin by orogastric gavage. Feeding with the listed diets started on day 0 and continued to the end of study. On day 14, rats were injected with complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) to induce arthritis. Arthritis activity was evaluated by the biochemical parameters and paw thickness. Biochemical assay for fibrinogen (Fn), serum amyloid A (SAA), and TNF-α and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (α1AGp) was performed on day 21, 28, and 35 (7, 14 and 21 days post RA induction), respectively.
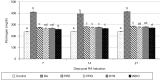
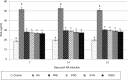
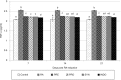
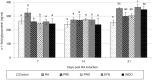
Results: Pretreatment with PRE, PRO, and SYN diets significantly inhibits SAA and Fn production in arthritic rats (P < 0.001). A significant decrease in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, was seen in the PRE, PRO, and SYN groups (P < 0.001), which was similar to the anti-inflammatory effect of indomethacin. Furthermore, no significant anti-inflammatory effects were observed following different treatments using α1 AGp as an RA indicator. Pretreatment with all supplied diets significantly inhibited the development of paw swelling induced by CFA (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The results of this study indicate that the oral intake of probiotic B. coagulans and prebiotic inulin can improve the biochemical and clinical parameters of induced RA in rat.
Keywords: Bacillus coagulans; animal model; inulin; rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effects of probiotic, prebiotic and synbiotic diets containing Bacillus coagulans and inulin on rat intestinal microbiota.Iran J Vet Res. 2015 Summer;16(3):267-73. Iran J Vet Res. 2015. PMID: 27175187 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of synbiotic diets of Bacillus coagulans, Lactobacillus plantarum and inulin against acute cadmium toxicity in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jun 5;17(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1803-3. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28583137 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus coagulans in Combination with Chitooligosaccharides Regulates Gut Microbiota and Ameliorates the DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0064122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00641-22. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35900082 Free PMC article.
-
Synbiotic supplementation with prebiotic green banana resistant starch and probiotic Bacillus coagulans spores ameliorates gut inflammation in mouse model of inflammatory bowel diseases.Eur J Nutr. 2020 Dec;59(8):3669-3689. doi: 10.1007/s00394-020-02200-9. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Eur J Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32067099 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the dual nature of Bacillus (Weizmannia) coagulans for sustainable production of biomaterials and development of functional food.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Apr;17(4):e14449. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14449. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38593329 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiome-immune interactions and their role in rheumatoid arthritis development.PeerJ. 2024 Jul 11;12:e17477. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17477. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39006008 Free PMC article.
-
The gut-brain axis in ischemic stroke: its relevance in pathology and as a therapeutic target.Neurol Res Pract. 2022 Nov 14;4(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s42466-022-00222-8. Neurol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 36401322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Cells to Environment: Exploring the Interplay between Factors Shaping Bone Health and Disease.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Aug 25;59(9):1546. doi: 10.3390/medicina59091546. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37763665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probiotic Supplementation for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Promising Adjuvant Therapy in the Gut Microbiome Era.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 23;12:711788. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.711788. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34366867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human in vivo assessment of the survival and germination of Heyndrickxia coagulans SNZ1969 spores delivered via gummy candies.Curr Res Food Sci. 2024 Jun 18;9:100793. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100793. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 39071473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vitetta L, Sali A. Probiotics, prebiotics and gastrointestinal health. Med Today. 2008;9:65–70.
-
- Baharav E, Mor F, Halpern M, Weinberger A. Lactobacillus GG bacteria ameliorate arthritis in Lewis rats. J Nutr. 2004;134:1964–9. - PubMed
-
- Kano H, Kaneko T, Kaminogawa S. Oral intake of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1 prevents collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Food Prot. 2002;65:153–60. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

