Commentary: Two-sample Mendelian randomization: opportunities and challenges
- PMID: 27427429
- PMCID: PMC5005949
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyw127
Commentary: Two-sample Mendelian randomization: opportunities and challenges
Figures
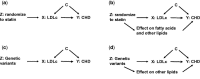
i. that the IV ‘Z’ (randomization to statins in Figure 1 a and genetic variants related to LDLc in Figure 1 c) is (or is plausibly) causally related to the risk factor (LDLc in all figures);
ii. that confounding factors for the risk factor-outcome ‘X’-’Y’ association (here LDLc on CHD in all figures) are not related to the instrumental variable;
iii. that the instrumental variable ‘Z’ only affects the outcome ‘Y’ (CHD) through its effect on the risk factor ‘X’ (LDLc).
Comment on
-
Mendelian randomization study of adiposity-related traits and risk of breast, ovarian, prostate, lung and colorectal cancer.Int J Epidemiol. 2016 Jun;45(3):896-908. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyw129. Epub 2016 Jul 17. Int J Epidemiol. 2016. PMID: 27427428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davey Smith G, Ebrahim S . ‘Mendelian randomization’: can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int J Epidemiol 2003. ; 32 : 1 – 22 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

