Interactions of Pleckstrin Homology Domains with Membranes: Adding Back the Bilayer via High-Throughput Molecular Dynamics
- PMID: 27427480
- PMCID: PMC4975593
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2016.06.002
Interactions of Pleckstrin Homology Domains with Membranes: Adding Back the Bilayer via High-Throughput Molecular Dynamics
Abstract
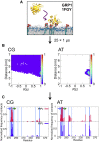
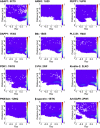
A molecular simulation pipeline for determining the mode of interaction of pleckstrin homology (PH) domains with phosphatidylinositol phosphate (PIP)-containing lipid bilayers is presented. We evaluate our methodology for the GRP1 PH domain via comparison with structural and biophysical data. Coarse-grained simulations yield a 2D density landscape for PH/membrane interactions alongside residue contact profiles. Predictions of the membrane localization and interactions of 13 PH domains reveal canonical, non-canonical, and dual PIP-binding sites on the proteins. Thus, the PH domains associate with the PIP molecules in the membrane via a highly positively charged loop. Some PH domains exhibit modes of interaction with PIP-containing membranes additional to this canonical binding mode. All 13 PH domains cause a degree of local clustering of PIP molecules upon binding to the membrane. This provides a global picture of PH domain interactions with membranes. The high-throughput approach could be extended to other families of peripheral membrane proteins.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Association of Peripheral Membrane Proteins with Membranes: Free Energy of Binding of GRP1 PH Domain with Phosphatidylinositol Phosphate-Containing Model Bilayers.J Phys Chem Lett. 2016 Apr 7;7(7):1219-24. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b00153. Epub 2016 Mar 17. J Phys Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 26977543 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and lipid-binding properties of the kindlin-3 pleckstrin homology domain.Biochem J. 2017 Feb 15;474(4):539-556. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160791. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 27974389 Free PMC article.
-
Modes of Interaction of Pleckstrin Homology Domains with Membranes: Toward a Computational Biochemistry of Membrane Recognition.J Mol Biol. 2018 Feb 2;430(3):372-388. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.12.011. Epub 2017 Dec 20. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29273202
-
The energetics of protein-lipid interactions as viewed by molecular simulations.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Feb 28;48(1):25-37. doi: 10.1042/BST20190149. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 31872229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational and theoretical approaches for studies of a lipid recognition protein on biological membranes.Biophys Physicobiol. 2017 Oct 26;14:153-160. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.14.0_153. eCollection 2017. Biophys Physicobiol. 2017. PMID: 29159013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Binding of Ca2+-independent C2 domains to lipid membranes: A multi-scale molecular dynamics study.Structure. 2021 Oct 7;29(10):1200-1213.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2021.05.011. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Structure. 2021. PMID: 34081910 Free PMC article.
-
Multiscale Simulations of Biological Membranes: The Challenge To Understand Biological Phenomena in a Living Substance.Chem Rev. 2019 May 8;119(9):5607-5774. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00538. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Chem Rev. 2019. PMID: 30859819 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Lipid-Protein Interactions and Lipid-Mediated Modulation of Membrane Protein Function through Molecular Simulation.Chem Rev. 2019 May 8;119(9):6086-6161. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00608. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Chem Rev. 2019. PMID: 30978005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphosphoinositide-Binding Domains: Insights from Peripheral Membrane and Lipid-Transfer Proteins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1111:77-137. doi: 10.1007/5584_2018_288. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30483964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two cooperative binding sites sensitize PI(4,5)P2 recognition by the tubby domain.Sci Adv. 2022 Sep 9;8(36):eabp9471. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abp9471. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36070381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson K.E., Coadwell J., Stephens L.R., Hawkins P.T. Translocation of PDK-1 to the plasma membrane is important in allowing PDK-1 to activate protein kinase B. Curr. Biol. 1998;8:684–691. - PubMed
-
- Arai N., Akimoto T., Yamamoto E., Yasui M., Yasuoka K. Poisson property of the occurrence of flip-flops in a model membrane. J. Chem. Phys. 2014;140:064901. - PubMed
-
- Balla T. Inositol-lipid binding motifs: signal integrators through protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions. J. Cell Sci. 2005;118:2093–2104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

