Corticosteroids for Bell's palsy (idiopathic facial paralysis)
- PMID: 27428352
- PMCID: PMC6457861
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001942.pub5
Corticosteroids for Bell's palsy (idiopathic facial paralysis)
Abstract
Background: Inflammation and oedema of the facial nerve are implicated in causing Bell's palsy. Corticosteroids have a potent anti-inflammatory action that should minimise nerve damage. This is an update of a review first published in 2002 and last updated in 2010.
Objectives: To determine the effectiveness and safety of corticosteroid therapy in people with Bell's palsy.
Search methods: On 4 March 2016, we searched the Cochrane Neuromuscular Specialised Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, EMBASE and LILACS. We reviewed the bibliographies of the randomised trials and contacted known experts in the field to identify additional published or unpublished trials. We also searched clinical trials registries for ongoing trials.
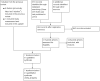
Selection criteria: Randomised trials and quasi-randomised trials comparing different routes of administration and dosage schemes of corticosteroid or adrenocorticotrophic hormone therapy versus a control group receiving no therapy considered effective for this condition, unless the same therapy was given in a similar way to the experimental group.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard Cochrane methodology. The main outcome of interest was incomplete recovery of facial motor function (i.e. residual facial weakness). Secondary outcomes were cosmetically disabling persistent sequelae, development of motor synkinesis or autonomic dysfunction (i.e. hemifacial spasm, crocodile tears) and adverse effects of corticosteroid therapy manifested during follow-up.
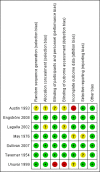
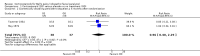
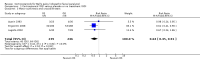
Main results: We identified seven trials, with 895 evaluable participants for this review. All provided data suitable for the primary outcome meta-analysis. One of the trials was new since the last version of this Cochrane systematic review. Risk of bias in the older, smaller studies included some unclear- or high-risk assessments, whereas we deemed the larger studies at low risk of bias. Overall, 79/452 (17%) participants allocated to corticosteroids had incomplete recovery of facial motor function six months or more after randomisation; significantly fewer than the 125/447 (28%) in the control group (risk ratio (RR) 0.63, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.50 to 0.80, seven trials, n = 895). The number of people who need to be treated with corticosteroids to avoid one incomplete recovery was 10 (95% CI 6 to 20). The reduction in the proportion of participants with cosmetically disabling sequelae six months after randomisation was very similar in the corticosteroid and placebo groups (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.40 to 2.29, two trials, n = 75, low-quality evidence). However, there was a significant reduction in motor synkinesis during follow-up in participants receiving corticosteroids (RR 0.64, 95% CI 0.45 to 0.91, three trials, n = 485, moderate-quality evidence). Three studies explicitly recorded the absence of adverse effects attributable to corticosteroids. One trial reported that three participants receiving prednisolone had temporary sleep disturbances and two trials gave a detailed account of adverse effects occurring in 93 participants, all non-serious; the combined analysis of data from these three trials found no significant difference in adverse effect rates between people receiving corticosteroids and people receiving placebo (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.71 to 1.51, n = 715).
Authors' conclusions: The available moderate- to high-quality evidence from randomised controlled trials showed significant benefit from treating Bell's palsy with corticosteroids.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures






Update of
-
Corticosteroids for Bell's palsy (idiopathic facial paralysis).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Mar 17;(3):CD001942. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001942.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 18;7:CD001942. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001942.pub5. PMID: 20238317 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Austin 1993 {published data only}
-
- Austin JR, Peskind SP, Austin SG, Rice DH. Idiopathic facial nerve paralysis: a randomized double blind controlled study of placebo versus prednisone. Laryngoscope 1993;103(12):1326‐33. [PUBMED: 8246650] - PubMed
Engström 2008 {published data only}
-
- Axelsson S, Berg T, Jonsson L, Engström M, Kanerva M, Stjernquist‐Desatnik A. Bell's palsy ‐ the effect of prednisolone and/or valaciclovir versus placebo in relation to baseline severity in a randomised controlled trial. Clinical Otolaryngology 2012;37(4):283‐90. [EMBASE: 2012510516] - PubMed
-
- Berg T, Bylund N, Marsk E, Jonsson L, Kanerva M, Hultcrantz M, et al. The effect of prednisolone on sequelae in Bell's palsy. Archives of Otolaryngology ‐ Head & Neck Surgery 2012;138(5):445‐9. [PUBMED: 22652942] - PubMed
-
- Engström M, Berg T, Stjemquist‐Desatnik A, Axelsson S, Pitkäranta A, Hultcrantz M, et al. Prednisolone and valaciclovir in Bell's palsy: a randomised double‐blind, placebo controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet Neurology 2008;7(11):993‐1000. [PUBMED: 18849193] - PubMed
Lagalla 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lagalla G, Logullo F, Bella P, Provinciali F, Ceravolo MG. Influence of early high‐dose steroid treatment on Bell's palsy evolution. Neurological Sciences 2002;23(3):107‐12. [PUBMED: 12391494] - PubMed
May 1976 {published data only}
-
- May M, Wette R, Hardin WB Jr, Sullivan J. The use of steroids in Bell's palsy: a prospective controlled study. Laryngoscope 1976;86(8):1111‐22. [PUBMED: 781439] - PubMed
Sullivan 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sullivan FM, Swan IRC, Donnan PT, Morrison JM, Smith BH, McKinstry B, et al. Early treatment with prednisolone or acyclovir in Bell´s Palsy. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;357(16):1598‐607. [PUBMED: 17942873] - PubMed
Taverner 1954 {published data only}
-
- Taverner D. Cortisone treatment of Bell's palsy. Lancet 1954;264(6847):1052‐4. [PUBMED: 13213115] - PubMed
Unuvar 1999 {published data only}
-
- Unuvar E, Oguz F, Sidal M, Kilic A. Corticosteroid treatment of childhood Bell's palsy. Pediatric Neurology 1999;21(5):814‐6. [PUBMED: 10593672] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Akpinar 1979 {published data only}
-
- Akpinar S, Boga M, Yardim M. Steroid versus placebo treatments in cases of acute peripheral facial paralysis [Akut periferik fasiyel paralizi olgularinda steroid tedavisinin plasebo ile oranlanmasi]. Bulletin of Gulhane Military Medical Academy 1979;21:45‐51.
Bento 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bento RF, Bogar P, Lorenzi MC. Treatment comparison between dexamethasone and placebo for idiopathic facial palsy. European Archives of Oto‐Rhino‐Laryngology 1994;suppl:S535‐6. [PUBMED: 10774443] - PubMed
-
- Bento RF, Lorenzi MC, Bogar P, Marone SA, Minili A. Comparison between dexametasone and placebo for idiopathic facial palsy [Comparacao entre a dexametasona e placebo no tratamento da paralisia facial periferica idiopatica]. Revista Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia 1991;57:196‐202. [EMBASE: 92038773]
Brown 1982 {published data only}
-
- Brown JS. Bell's palsy: a 5 year review of 174 consecutive cases: an attempted double blind study. Laryngoscope 1982;92(12):1369‐73. [PUBMED: 6757616] - PubMed
Martinez 1990 {published data only}
-
- Martinez CG, Abarca B, Alvardo CL. Bell's palsy: evaluation of steroid treatment [Paralisis de Bell: Evaluacion del tratamiento esteroidal]. Boletin del hospital de San Juan de Dios 1990;37(1):13‐7.
Wolf 1978 {published data only}
-
- Wolf SM, Wagner JH, Davidson S, Forsythe A. Treatment of Bell palsy with prednisone: a prospective, randomized study. Neurology 1978;28(2):158‐61. [PUBMED: 340980] - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Babl 2015 {unpublished data only}
-
- Bell's palsy in children: a multi‐centre, double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled trial to determine whether prednisolone improves recovery at 1 month. Ongoing study 1 July 2015.
Additional references
Adour 1972
-
- Adour KK, Wingerd J, Bell DN, Manning JJ, Hurley JP. Prednisone treatment for idiopathic facial paralysis (Bell's palsy). New England Journal of Medicine 1972;287(25):1268‐72. - PubMed
Adour 1982
-
- Adour KK. Current concepts in neurology: diagnosis and management of facial paralysis. New England Journal of Medicine 1982;307(6):348‐51. - PubMed
Bateman 1992
-
- Bateman JE. Facial palsy. British Journal of Hospital Medicine 1992;47(6):430‐31. - PubMed
Brandenberg 1993
-
- Brandenberg NA, Annegers JF. Incidence and risk factors for Bell's palsy in Laredo, Texas. Neuroepidemiology 1993;12(6):313‐25. - PubMed
Burgess 1984
-
- Burgess LP, Yim DW, Lepore ML. Bell's palsy: the controversy revisited. Laryngoscope 1984;94(11 pt 1):1472‐6. - PubMed
de Almeida 2009
-
- Almeida JR, Al Khabori M, Guyatt GH, Witterick IJ, Lin VYW, Nedzelski JM, et al. Combined corticosteroid and antiviral treatment for Bell palsy: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. JAMA 2009;302(9):985‐93. - PubMed
Dollery 1999
-
- Dollery C. Therapeutic Drugs. 2nd Edition. Vol. 2, Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1999. [ISBN: 0443051488 (2 volumes)]
Egger 2007
-
- Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG. Systematic Reviews in Health Care: Meta‐Analysis in context. 6th Edition. London: BMJ Books, 2007.
Gagyor 2015
GRADEpro 2008 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University. GRADEpro. Version 3.2 for Windows. McMaster University, 2008.
Grogan 2001
-
- Grogan PM, Gronseth GS. Practice parameter: steroids, acyclovir, and surgery for Bell's palsy (an evidence‐based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2001;56(7):830‐6. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Katusic 1986
-
- Katusic SK, Beard CM, Wiederholt WC, Bergstrahl EJ, Kurland LT. Incidence, clinical features, and prognosis in Bell's palsy, Rochester, Minnesota. Annals of Neurology 1986;20(5):622‐7. - PubMed
Lackner 2010
-
- Lackner A, Kessler HH, Walch C, Quasthoff S, Raggam RB. Early and reliable detection of herpes simplex virus type 1 and varicella zoster virus DNAs in oral fluid of patients with idiopathic peripheral facial nerve palsy: decision support regarding antiviral treatment?. Journal of Medical Virology 2010;82(9):1582‐5. - PubMed
Madhok 2009
-
- Madhok V, Falk G, Fahey T, Sullivan F. Prescribe prednisolone alone for Bell's palsy diagnosed within 72 hours of symptom onset. BMJ 2009;338:255. - PubMed
Martyn 1997
Morales 2013
Murakami 1996
-
- Murakami S, Mizobuchi M, Nakashiro Y, Doi T, Hato N, Yanagihara N. Bell palsy and herpes simplex virus: identification of viral DNA in endoneurial fluid and muscle. Annals of Internal Medicine 1996;124(1 pt 1):27‐30. - PubMed
Niparko 1993
-
- Niparko JK, Mattox DE. Bell's palsy and herpes zoster oticus. In: Johnson RT, Griffin JW editor(s). Current Therapy in Neurologic Disease. 4th Edition. St. Louis, MO: BC Decker, 1993:355‐61. [ISBN: 0801677300]
Peitersen 1982
-
- Peitersen E. The natural history of Bell's palsy. American Journal of Otology 1982;4(2):107‐11. - PubMed
Peitersen 2002
-
- Peitersen E. Bell's palsy: the spontaneous course of 2,500 peripheral facial nerve palsies of different etiologies. Acta Otolaryngologica Supplementum 2002;549:4‐30. - PubMed
Prescott 1988
-
- Prescott CA. Idiopathic facial nerve palsy (the effect of treatment with steroids). Journal of Laryngology & Otology 1988;102(5):403‐7. - PubMed
Ramsey 2000
-
- Ramsey MJ, DerSimonian R, Holtel MR, Burgess LP. Corticosteroid treatment for idiopathic facial nerve palsy: a meta analysis. Laryngoscope 2000;110(3 pt 1):335‐41. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Shafshak 1994
-
- Shafshak TS, Essa AY, Bakey FA. The possible contributing factors for the success of steroid therapy in Bell's palsy: a clinical and electrophysiological study. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1994;108(11):940‐3. - PubMed
Victor 1994
-
- Victor M, Martin J. Disorders of the cranial nerves. In: Isselbacher KJ, Wilson J, Fauci A, Braunwald E, Martin J, Kasper D editor(s). Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 13th Edition. New York: McGraw‐Hill, 1994:2347‐52. [ISBN: 0070323704]
Williamson 1996
Yanagihara 1988
-
- Yanagihara N, Yumoto E, Shibahara T. Familial Bell's palsy: analysis of 25 families. Annals of Otology, Rhinology and Laryngology 1988;137(Suppl):8‐10. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Salinas 2002
Salinas 2004
Salinas 2009
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

