A Nexus Consisting of Beta-Catenin and Stat3 Attenuates BRAF Inhibitor Efficacy and Mediates Acquired Resistance to Vemurafenib
- PMID: 27428425
- PMCID: PMC4919613
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.04.037
A Nexus Consisting of Beta-Catenin and Stat3 Attenuates BRAF Inhibitor Efficacy and Mediates Acquired Resistance to Vemurafenib
Abstract
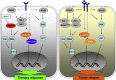
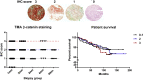
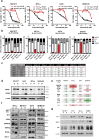
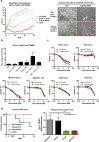
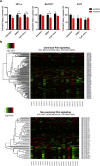
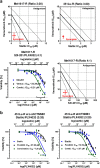
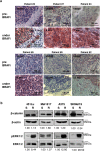
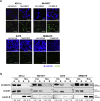
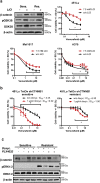
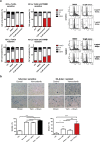
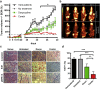
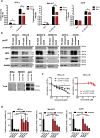
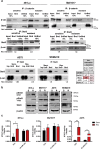
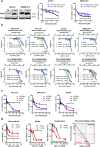
Acquired resistance to second generation BRAF inhibitors (BRAFis), like vemurafenib is limiting the benefits of long term targeted therapy for patients with malignant melanomas that harbor BRAF V600 mutations. Since many resistance mechanisms have been described, most of them causing a hyperactivation of the MAPK- or PI3K/AKT signaling pathways, one potential strategy to overcome BRAFi resistance in melanoma cells would be to target important common signaling nodes. Known factors that cause secondary resistance include the overexpression of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), alternative splicing of BRAF or the occurrence of novel mutations in MEK1 or NRAS. In this study we show that β-catenin is stabilized and translocated to the nucleus in approximately half of the melanomas that were analyzed and which developed secondary resistance towards BRAFi. We further demonstrate that β-catenin is involved in the mediation of resistance towards vemurafenib in vitro and in vivo. Unexpectedly, β-catenin acts mainly independent of the TCF/LEF dependent canonical Wnt-signaling pathway in resistance development, which partly explains previous contradictory results about the role of β-catenin in melanoma progression and therapy resistance. We further demonstrate that β-catenin interacts with Stat3 after chronic vemurafenib treatment and both together cooperate in the acquisition and maintenance of resistance towards BRAFi.
- •
Melanoma cells with acquired resistance frequently express high amounts of β-catenin.
- •
In these cells a hyper-activation of Stat3 co-occurs leading to an interaction with β-catenin.
- •
Such BRAFi resistant melanoma cells are sensitive to knockdown of β-catenin and Stat3 or pharmacologic Stat3 inhibition.
Treatment with BRAF inhibitors is the basis of the standard therapy for melanoma patients with BRAFV600 mutated metastases. Although this therapy achieves impressive short-term benefit, many patients suffer from relapse after several months of treatment even if the therapy is combined with MEK inhibitors. The development of therapy resistant tumor cells is a multifactorial transformation and several cellular mechanisms are already described. Here, we found an interaction of two well-known tumor-associated proteins, namely β-catenin and Stat3 in resistant metastatic melanoma cells. Patient data support that these proteins are involved in the resistance to BRAF inhibitor therapy.
Keywords: BRAF; Melanoma; Resistance; Stat3; Vemurafenib; β-catenin.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors.J Clin Invest. 2014 Jul;124(7):2877-90. doi: 10.1172/JCI70156. Epub 2014 May 27. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24865425 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacodynamic effects and mechanisms of resistance to vemurafenib in patients with metastatic melanoma.J Clin Oncol. 2013 May 10;31(14):1767-74. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.44.7888. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23569304 Clinical Trial.
-
A new water soluble MAPK activator exerts antitumor activity in melanoma cells resistant to the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 May 1;95(1):16-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25795251
-
BRAF as a target for cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Mar;11(3):285-95. doi: 10.2174/187152011795347469. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21426297 Review.
-
The discovery of vemurafenib for the treatment of BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016 Sep;11(9):907-16. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2016.1201057. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27327499 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antiangiogenic activity of the penicillin derivative TAP7f in melanoma.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 Mar;101(3):249-263. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02287-7. Epub 2023 Jan 23. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 36688961
-
Quantitative Proteomics Links the Intermediate Filament Nestin to Resistance to Targeted BRAF Inhibition in Melanoma Cells.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 Jun;18(6):1096-1109. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001302. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 30890564 Free PMC article.
-
A targeted genomic alteration analysis predicts survival of melanoma patients under BRAF inhibitors.Oncotarget. 2019 Mar 1;10(18):1669-1687. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26707. eCollection 2019 Mar 1. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 30899440 Free PMC article.
-
Melanoma cells resistant towards MAPK inhibitors exhibit reduced TAp73 expression mediating enhanced sensitivity to platinum-based drugs.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 11;9(9):930. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0952-8. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30206212 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of p90 ribosomal S6 kinases disrupts melanoma cell growth and immune evasion.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 19;42(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02755-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37464364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel E.V., Basile K.J., Kugel C.H., Witkiewicz A.K., Le K., Amaravadi R.K., Karakousis G.C., Xu X., Xu W., Schuchter L.M., Lee J.B., Ertel A., Fortina P., Aplin A.E. Melanoma adapts to RAF/MEK inhibitors through FOXD3-mediated upregulation of ERBB3. J. Clin. Invest. 2013;123:2155–2168. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

