Targeted inhibition of oncogenic miR-21 maturation with designed RNA-binding proteins
- PMID: 27428511
- PMCID: PMC4990487
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.2128
Targeted inhibition of oncogenic miR-21 maturation with designed RNA-binding proteins
Abstract
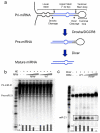
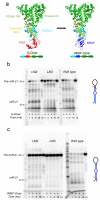
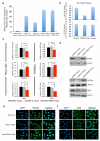
The RNA recognition motif (RRM) is the largest family of eukaryotic RNA-binding proteins. Engineered RRMs with well-defined specificity would provide valuable tools and an exacting test of the current understanding of specificity. We have redesigned the specificity of an RRM using rational methods and demonstrated retargeting of its activity in cells. We engineered the conserved RRM of human Rbfox proteins to specifically bind to the terminal loop of a microRNA precursor (pre-miR-21) with high affinity and inhibit its processing by Drosha and Dicer. We further engineered Giardia Dicer by replacing its PAZ domain with the designed RRM. The reprogrammed enzyme degrades pre-miR-21 specifically in vitro and suppresses mature miR-21 levels in cells, which results in increased expression of the tumor suppressor PDCD4 and significantly decreased viability for cancer cells. The results demonstrate the feasibility of rationally engineering the sequence-specificity of RRMs and of using this ubiquitous platform for diverse biological applications.
Figures
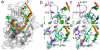

References
Methods-only References
-
- Price SR, Oubridge C, Varani G, Nagai K. Preparation of RNA–protein complexes for X-ray crystallography and NMR. In: Smith C, editor. RNA–Protein Interaction: Practical Approach. Oxford University Press; Oxford: 1998. pp. 37–74.
-
- Wilkinson KA, Merino EJ, Weeks KM. Selective 2′-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension (SHAPE): quantitative RNA structure analysis at single nucleotide resolution. Nature Protoc. 2006;1:1610–1616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

