Risk of new onset autoimmune disease in 9- to 25-year-old women exposed to human papillomavirus-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine in the United Kingdom
- PMID: 27428517
- PMCID: PMC5137515
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2016.1199308
Risk of new onset autoimmune disease in 9- to 25-year-old women exposed to human papillomavirus-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine in the United Kingdom
Abstract
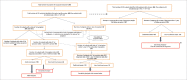
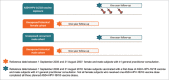
To assess the risk of autoimmune disease (AD) in 9-25 year-old women within 1 year after the first AS04-HPV-16/18vaccine dose, a retrospective, observational database cohort study was conducted using CPRD GOLD. From CPRD GOLD 4 cohorts (65,000 subjects each) were retrieved: 1 exposed female cohort (received ≥1 AS04-HPV-16/18 vaccine dose between Sep2008-Aug2010) and 3 unexposed cohorts: historical female (Sep2005-Aug2007), concurrent male, and historical male. Co-primary endpoints were confirmed neuroinflammatory/ophthalmic AD and other AD, secondary endpoints were confirmed individual AD. Risk of new onset of AD was compared between cohorts (reference: historical cohort) using Poisson regression. The main analysis using confirmed cases showed no neuroinflammatory/ophthalmic AD cases in the female exposed cohort. Incidence rate ratio (IRR) (95% CI) of other AD was 1.41 (0.86 to 2.31) in female and 1.77 (0.94 to 3.35) in male cohorts when compared to the female and male historical cohort, respectively. Secondary endpoints were evaluated for diseases with >10 cases, which were Crohn's disease (IRR: 1.21 [0.37 to 3.95] for female and 4.22 [0.47 to 38.02] for male cohorts), autoimmune thyroiditis (IRR: 3.75 [1.25 to 11.31] for female and no confirmed cases for male cohorts) and type 1 diabetes (IRR: 0.30 [0.11 to 0.83] for female and 2.46 [1.08 to 5.60] for male cohorts). Analysis using confirmed and non-confirmed cases showed similar results, except for autoimmune thyroiditis in females, IRR: 1.45 (0.79 to 2.64). There was no evidence of an increased risk of AD in women aged 9 to 25 years after AS04-HPV-16/18 vaccination.
Keywords: autoimmune conditions; human papilloma virus; human papillomavirus vaccine; post-licensure safety study; vaccination; vaccine safety.
Figures
References
-
- Stanley M. Pathology and epidemiology of HPV infection in females. Gynecol Oncol 2010; 117:S5-10; PMID:20304221; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2010.01.024 - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Sanjose S, Quint WG, Alemany L, Geraets DT, Klaustermeier JE, Lloveras B, Tous S, Felix A, Bravo LE, Shin HR, et al.. Human papillomavirus genotype attribution in invasive cervical cancer: a retrospective cross-sectional worldwide study. Lancet Oncol 2010; 11:1048-56; PMID:20952254; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70230-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lehtinen M, Paavonen J, Wheeler CM, Jaisamrarn U, Garland SM, Castellsague X, Skinner SR, Apter D, Naud P, Salmeron J, et al.. Overall efficacy of HPV-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine against grade 3 or greater cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: 4-year end-of-study analysis of the randomised, double-blind PATRICIA trial. Lancet Oncol 2012; 13:89-99; PMID:22075171; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70286-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Skinner SR, Szarewski A, Romanowski B, Garland SM, Lazcano-Ponce E, Salmeron J, Del Rosario-Raymundo MR, Verheijen RH, Quek SC, da Silva DP, et al.. Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of the human papillomavirus 16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine in women older than 25 years: 4-year interim follow-up of the phase 3, double-blind, randomised controlled VIVIANE study. Lancet 2014; 384:2213-27; PMID:25189358; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60920-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wheeler CM, Castellsague X, Garland SM, Szarewski A, Paavonen J, Naud P, Salmeron J, Chow SN, Apter D, Kitchener H, et al.. Cross-protective efficacy of HPV-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine against cervical infection and precancer caused by non-vaccine oncogenic HPV types: 4-year end-of-study analysis of the randomised, double-blind PATRICIA trial. Lancet Oncol 2012; 13:100-10; PMID:22075170; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70287-X - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
