PARP Inhibitors in Clinical Use Induce Genomic Instability in Normal Human Cells
- PMID: 27428646
- PMCID: PMC4948780
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159341
PARP Inhibitors in Clinical Use Induce Genomic Instability in Normal Human Cells
Abstract
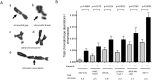
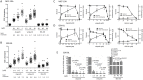
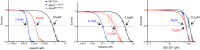
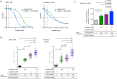
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) are the first proteins involved in cellular DNA repair pathways to be targeted by specific inhibitors for clinical benefit. Tumors harboring genetic defects in homologous recombination (HR), a DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair pathway, are hypersensitive to PARP inhibitors (PARPi). Early phase clinical trials with PARPi have been promising in patients with advanced BRCA1 or BRCA2-associated breast, ovary and prostate cancer and have led to limited approval for treatment of BRCA-deficient ovary cancer. Unlike HR-defective cells, HR-proficient cells manifest very low cytotoxicity when exposed to PARPi, although they mount a DNA damage response. However, the genotoxic effects on normal human cells when agents including PARPi disturb proficient cellular repair processes have not been substantially investigated. We quantified cytogenetic alterations of human cells, including primary lymphoid cells and non-tumorigenic and tumorigenic epithelial cell lines, exposed to PARPi at clinically relevant doses by both sister chromatid exchange (SCE) assays and chromosome spreading. As expected, both olaparib and veliparib effectively inhibited poly-ADP-ribosylation (PAR), and caused marked hypersensitivity in HR-deficient cells. Significant dose-dependent increases in SCEs were observed in normal and non-tumorigenic cells with minimal residual PAR activity. Clinically relevant doses of the FDA-approved olaparib led to a marked increase of SCEs (5-10-fold) and chromatid aberrations (2-6-fold). Furthermore, olaparib potentiated SCE induction by cisplatin in normal human cells. Our data have important implications for therapies with regard to sustained genotoxicity to normal cells. Genomic instability arising from PARPi warrants consideration, especially if these agents will be used in people with early stage cancers, in prevention strategies or for non-oncologic indications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kim MY, Zhang T, Kraus WL (2005) Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation by PARP-1: 'PAR-laying' NAD+ into a nuclear signal. Genes Dev 19: 1951–1967. - PubMed
-
- Schreiber V, Ame JC, Dolle P, Schultz I, Rinaldi B, et al. (2002) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-2 (PARP-2) is required for efficient base excision DNA repair in association with PARP-1 and XRCC1. J Biol Chem 277: 23028–23036. - PubMed
-
- Masutani M, Nozaki T, Nishiyama E, Shimokawa T, Tachi Y, et al. (1999) Function of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in response to DNA damage: gene-disruption study in mice. Mol Cell Biochem 193: 149–152. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

