Specific patterns of PIWI-interacting small noncoding RNA expression in dysplastic liver nodules and hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27429044
- PMCID: PMC5342370
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10567
Specific patterns of PIWI-interacting small noncoding RNA expression in dysplastic liver nodules and hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
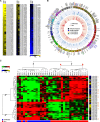
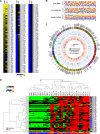
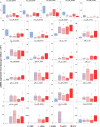
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the result of a stepwise process, often beginning with development within a cirrhotic liver of premalignant lesions, morphologically characterized by low- (LGDN) and high-grade (HGDN) dysplastic nodules. PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs (sncRNAs), 23-35 nucleotide-long, exerting epigenetic and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Recently the PIWI-piRNA pathway, best characterized in germline cells, has been identified also in somatic tissues, including stem and cancer cells, where it influences key cellular processes.Small RNA sequencing was applied to search for liver piRNAs and to profile their expression patterns in cirrhotic nodules (CNs), LGDN, HGDN, early HCC and progressed HCC (pHCC), analyzing 55 samples (14 CN, 9 LGDN, 6 HGDN, 6 eHCC and 20 pHCC) from 17 patients, aiming at identifying possible relationships between these sncRNAs and liver carcinogenesis. We identified a 125 piRNA expression signature that characterize HCC from matched CNs, correlating also to microvascular invasion in HCC. Functional analysis of the predicted RNA targets of deregulated piRNAs indicates that these can target key signaling pathways involved in hepatocarcinogenesis and HCC progression, thereby affecting their activity. Interestingly, 24 piRNAs showed specific expression patterns in dysplastic nodules, respect to cirrhotic liver and/or pHCC.The results demonstrate that the PIWI-piRNA pathway is active in human liver, where it represents a new player in the molecular events that characterize hepatocarcinogenesis, from early stages to pHCC. Furthermore, they suggest that piRNAs might be new disease biomarkers, useful for differential diagnosis of dysplastic and neoplastic liver lesions.
Keywords: hepatocarcinogenesis; hepatocellular carcinoma; piRNAs; small non-coding RNA; smallRNA-seq.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- Nault JC, Calderaro J, Di Tommaso L, Balabaud C, Zafrani ES, Bioulac-Sage P, Roncalli M, Zucman-Rossi J. Telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutation is an early somatic genetic alteration in the transformation of premalignant nodules in hepatocellular carcinoma on cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2014;60:1983–1992. - PubMed
-
- Whittaker S, Marais R, Zhu AX. The role of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2010;29:4989–5005. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

