Photoacoustic Imaging in Oncology: Translational Preclinical and Early Clinical Experience
- PMID: 27429141
- PMCID: PMC4976462
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.16151414
Photoacoustic Imaging in Oncology: Translational Preclinical and Early Clinical Experience
Abstract
Photoacoustic imaging has evolved into a clinically translatable platform with the potential to complement existing imaging techniques for the management of cancer, including detection, characterization, prognosis, and treatment monitoring. In photoacoustic imaging, tissue is optically excited to produce ultrasonographic images that represent a spatial map of optical absorption of endogenous constituents such as hemoglobin, fat, melanin, and water or exogenous contrast agents such as dyes and nanoparticles. It can therefore provide functional and molecular information that allows noninvasive soft-tissue characterization. Photoacoustic imaging has matured over the years and is currently being translated into the clinic with various clinical studies underway. In this review, the current state of photoacoustic imaging is presented, including techniques and instrumentation, followed by a discussion of potential clinical applications of this technique for the detection and management of cancer. (©) RSNA, 2016.
Figures
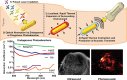
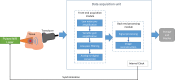


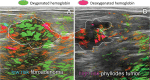
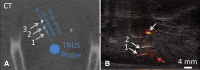



References
-
- Manohar S, van Apeldoorn A, Taruttis WS. Photoacoustic imaging: cells make themselves heard. Nat Photonics 2015;9:216–218.
-
- Bell AG. Production of sound by radiant energy. Science 1881;2(49):242–253. - PubMed
-
- Wang LV, Wu HI. Biomedical optics, principles and imaging. J Biomed Opt 2008;13(4):049902.
-
- Oraevsky AA, Karabutov AA. Optoacoustic tomography. In: Vo-Dinh T, ed. Biomedical photonics handbook. Boca Raton, Fla: CRC, 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

