Obesity and cancer: inflammation bridges the two
- PMID: 27429211
- PMCID: PMC4992602
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2016.07.005
Obesity and cancer: inflammation bridges the two
Abstract
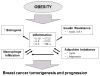
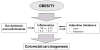
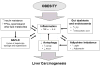
Obesity is a growing public health problem and affects 35% US adults. Obesity increases the risk of many cancer types and is associated with poor outcomes. Clinical management of cancer patients has been essentially the same between normal weight and obese individuals. Understanding causal mechanisms by which obesity drives cancer initiation and progression is essential for the development of novel precision therapy for obese cancer patients. One caveat is that various mechanisms have been proposed for different cancer types for their progression under obesity. Since obesity is known to have global impact on inflammation, here we will summarize recent literature and discuss the potential of inflammation being the common causal mechanism to promote cancer promotion across cancer types.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Martin-Rodriguez E, Guillen-Grima F, Marti A, Brugos-Larumbe A. Comorbidity associated with obesity in a large population: The APNA study. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2015;9:435–447. - PubMed
-
- Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1625–1638. - PubMed
-
- Amer A, Franchi L, Kanneganti TD, Body-Malapel M, Ozoren N, Brady G, Meshinchi S, Jagirdar R, Gewirtz A, Akira S, et al. Regulation of Legionella phagosome maturation and infection through flagellin and host Ipaf. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:35217–35223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

