Standards and Guidelines in Telemedicine and Telehealth
- PMID: 27429261
- PMCID: PMC4934495
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare2010074
Standards and Guidelines in Telemedicine and Telehealth
Abstract
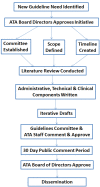
The development of guidelines and standards for telemedicine is an important and valuable process to help insure effective and safe delivery of quality healthcare. Some organizations, such as the American Telemedicine Association (ATA), have made the development of standards and guidelines a priority. The practice guidelines developed so far have been well received by the telemedicine community and are being adopted in numerous practices, as well as being used in research to support the practice and growth of telemedicine. Studies that utilize published guidelines not only help bring them into greater public awareness, but they also provide evidence needed to validate existing guidelines and guide the revision of future versions. Telemedicine will continue to grow and be adopted by more healthcare practitioners and patients in a wide variety of forms not just in the traditional clinical environments, and practice guidelines will be a key factor in fostering this growth. Creation of guidelines is important to payers and regulators as well as increasingly they are adopting and integrating them into regulations and policies. This paper will review some of the recent ATA efforts in developing telemedicine practice guidelines, review the role of research in guidelines development, review data regarding their use, and discuss some of areas where guidelines are still needed.
Keywords: guidelines; practice; research; standards; telemedicine.
Figures
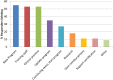
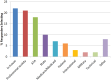
References
-
- Department of Health and Human Services Assessment of Approaches to Evaluating Telemedicine. [(accessed on 30 November 2013)]. Available online: http://aspe.hhs.gov/health/reports/AAET/aaet.htm/
-
- Institute of Medicine The Role of Telehealth in an Evolving Health Care Environment—Workshop Summary. [(accessed on 30 November 2013)]. Available online: http://www.iom.edu/Reports/2012/The-Role-of-Telehealth-in-an-Evolving-He... - PubMed
-
- Porter M.E. What is value in health care? NEJM. 2010;363:2477–2481. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

