Design of a Virtual Reality System for Affect Analysis in Facial Expressions (VR-SAAFE); Application to Schizophrenia
- PMID: 27429438
- PMCID: PMC6657800
- DOI: 10.1109/TNSRE.2016.2591556
Design of a Virtual Reality System for Affect Analysis in Facial Expressions (VR-SAAFE); Application to Schizophrenia
Abstract
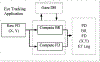
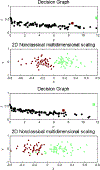
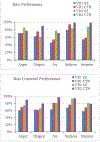
Schizophrenia is a life-long, debilitating psychotic disorder with poor outcome that affects about 1% of the population. Although pharmacotherapy can alleviate some of the acute psychotic symptoms, residual social impairments present a significant barrier that prevents successful rehabilitation. With limited resources and access to social skills training opportunities, innovative technology has emerged as a potentially powerful tool for intervention. In this paper, we present a novel virtual reality (VR)-based system for understanding facial emotion processing impairments that may lead to poor social outcome in schizophrenia. We henceforth call it a VR System for Affect Analysis in Facial Expressions (VR-SAAFE). This system integrates a VR-based task presentation platform that can minutely control facial expressions of an avatar with or without accompanying verbal interaction, with an eye-tracker to quantitatively measure a participants real-time gaze and a set of physiological sensors to infer his/her affective states to allow in-depth understanding of the emotion recognition mechanism of patients with schizophrenia based on quantitative metrics. A usability study with 12 patients with schizophrenia and 12 healthy controls was conducted to examine processing of the emotional faces. Preliminary results indicated that there were significant differences in the way patients with schizophrenia processed and responded towards the emotional faces presented in the VR environment compared with healthy control participants. The preliminary results underscore the utility of such a VR-based system that enables precise and quantitative assessment of social skill deficits in patients with schizophrenia.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Virtual faces as a tool to study emotion recognition deficits in schizophrenia.Psychiatry Res. 2010 Oct 30;179(3):247-52. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2009.11.004. Epub 2010 May 18. Psychiatry Res. 2010. PMID: 20483465
-
Understanding how adolescents with autism respond to facial expressions in virtual reality environments.IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph. 2013 Apr;19(4):711-20. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2013.42. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph. 2013. PMID: 23428456 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between facial emotion recognition, cognition and alexithymia in patients with schizophrenia: comparison of photographic and virtual reality presentations.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2012;181:88-92. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2012. PMID: 22954834
-
Emotion recognition via facial expression and affective prosody in schizophrenia: a methodological review.Clin Psychol Rev. 2002 Jul;22(6):789-832. doi: 10.1016/s0272-7358(02)00130-7. Clin Psychol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12214327 Review.
-
Brave new worlds--review and update on virtual reality assessment and treatment in psychosis.Schizophr Bull. 2014 Nov;40(6):1194-7. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbu125. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Schizophr Bull. 2014. PMID: 25193975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Virtual Reality and Psychedelics for the Treatment of Psychiatric Disease: A Systematic Literature Review.Clin Neuropsychiatry. 2020 Dec;17(6):365-380. doi: 10.36131/cnfioritieditore20200606. Clin Neuropsychiatry. 2020. PMID: 34909015 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the ecological validity of research on social cognition in schizophrenia: A systematic review of the literature.Schizophr Res Cogn. 2024 Oct 17;39:100333. doi: 10.1016/j.scog.2024.100333. eCollection 2025 Mar. Schizophr Res Cogn. 2024. PMID: 39498298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Choice of Leisure Activities by Adolescents and Adults With Internet Gaming Disorder: Development and Feasibility Study of a Virtual Reality Program.JMIR Serious Games. 2020 Dec 11;8(4):e18473. doi: 10.2196/18473. JMIR Serious Games. 2020. PMID: 33306033 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships between Nursing Students' Skill Mastery, Test Anxiety, Self-Efficacy, and Facial Expressions: A Preliminary Observational Study.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Feb 7;10(2):311. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10020311. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35206925 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Contagion and Emotional Mimicry in Individuals with Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 6;13(17):5296. doi: 10.3390/jcm13175296. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39274509 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hempel RJ, Tulen JH, van Beveren NJ, van Steenis HG, Mulder PG, and Hengeveld MW, “Physiological responsivity to emotional pictures in schizophrenia,” Journal of psychiatric research, vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 509–518, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Dawson ME and Nuechterlein KH, “Psychophysiological dysfunctions in the developmental course of schizophrenic disorders,” Schizophrenia Bulletin, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 204–232, 1984. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein AS, Frith CD, Gruzelier JH, Patterson T, Straube E, Venables PH, and Zahn TP, “An analysis of the skin conductance orienting response in samples of american, british, and german schizophrenics,” Biological Psychology, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 155–211, 1982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

