Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics, and Predictors of Patients with Thromboembolic Events in Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 27429563
- PMCID: PMC4944829
- DOI: 10.4137/CMC.S38151
Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics, and Predictors of Patients with Thromboembolic Events in Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Background: Several acute complications related to takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TTC) have been documented recently. However, the incidence and clinical significance of acute thromboembolic events in TTC is not well established.
Methods: A detailed investigation of the clinical characteristics and in-hospital complications of 114 consecutive patients diagnosed with TTC between January 2003 and September 2015 was carried out. This study was initiated to reveal the predictors, clinical significance, and short-term and long-term outcomes of patients with TTC associated with acute thromboembolic events on index presentation.
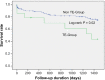
Results: The incidence of acute thromboembolic events related to TTC was around 12.2%, and these included ventricular thrombi, cerebrovascular events, retinal and brachial artery pathologies, renal, splenic, and aortic involvement. The most frequent complication on initial presentation was cardiogenic shock (20%) accompanied with pulmonary congestion (20%). Interestingly, patients experiencing thromboembolic events had higher C-reactive protein (CRP) levels as compared to the non-thromboembolic group (P = 0.02). Certain thromboembolic events were characterized by the presence of ST-segment elevation in electrocardiogram (P = 0.02). Chest pain was the primary symptom in these patients (P = 0.09). Furthermore, there was significant right ventricular involvement (as assessed by transthoracic echocardiography) in patients presenting with an acute thromboembolic event (P = 0.08). A Kaplan-Meier analysis indicated a significantly higher mortality rate over a mean follow-up of three years in the thromboembolic group than the non-thromboembolic group (log-rank, P = 0.02).
Conclusions: Our results confirmed the relative common occurrence of thromboembolic events in the setting of TTC. Inflammation might play an important role in the development of thromboembolic events, and a right ventricular involvement and ST-segment elevation could be positive predictors for this occurrence. In order to circumvent the risk of a negative outcome, it is recommended that an anticoagulation therapy be initiated in all high-risk patients.
Keywords: LV thrombus; stroke; takotsubo cardiomyopathy; thromboembolic events.
Figures
References
-
- Dote K, Sato H, Tateishi H, Uchida T, Ishihara M. Myocardial stunning due to simultaneous multivessel coronary spasms: a review of 5 cases. J Cardiol. 1991;21(2):203–14. - PubMed
-
- Elesber A, Lerman A, Bybee KA, et al. Myocardial perfusion in apical ballooning syndrome correlate of myocardial injury. Am Heart J. 2006;152(3):469, e9–13. - PubMed
-
- Brinjikji W, El-Sayed AM, Salka S. In-hospital mortality among patients with takotsubo cardiomyopathy: a study of the National Inpatient Sample 2008 to 2009. Am Heart J. 2012;164(2):215–21. - PubMed
-
- de Gregorio C, Cento D, Di Bella G, Coglitore S. Minor stroke in a takotsubo-like syndrome: a rare clinical presentation due to transient left ventricular thrombus. Int J Cardiol. 2008;130(2):e78–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous