Balancing macronutrient intake in a mammalian carnivore: disentangling the influences of flavour and nutrition
- PMID: 27429768
- PMCID: PMC4929903
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.160081
Balancing macronutrient intake in a mammalian carnivore: disentangling the influences of flavour and nutrition
Abstract
There is a large body of research demonstrating that macronutrient balancing is a primary driver of foraging in herbivores and omnivores, and more recently, it has been shown to occur in carnivores. However, the extent to which macronutrient selection in carnivores may be influenced by organoleptic properties (e.g. flavour/aroma) remains unknown. Here, we explore the roles of nutritional and hedonic factors in food choice and macronutrient balancing in a mammalian carnivore, the domestic cat. Using the geometric framework, we determined the amounts and ratio of protein and fat intake in cats allowed to select from combinations of three foods that varied in protein : fat (P : F) composition (approx. 10 : 90, 40 : 60 and 70 : 30 on a per cent energy basis) to which flavours of different 'attractiveness' (fish, rabbit and orange) were added. In two studies, in which animal and plant protein sources were used, respectively, the ratio and amounts of protein and fat intake were very consistent across all groups regardless of flavour combination, indicating regulation of both protein and fat intake. Our results suggest that macronutrient balancing rather than hedonistic rewards based on organoleptic properties of food is a primary driver of longer-term food selection and intake in domestic cats.
Keywords: carnivore; cats; food selection; geometric framework; hedonic; macronutrient.
Figures
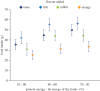
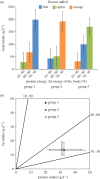
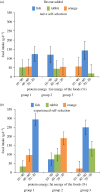

References
-
- Hewson-Hughes AK, Hewson-Hughes VL, Miller AT, Hall SR, Simpson SJ, Raubenheimer D. 2011. Geometric analysis of macronutrient selection in the adult domestic cat, Felis catus. J. Exp. Biol. 214, 1039–1041. (doi:10.1242/jeb.049429) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mayntz D, Nielsen VH, Sørensen A, Toft S, Raubenheimer D, Hejlesen C, Simpson SJ. 2009. Balancing of protein and lipid intake by a mammalian carnivore, the mink, Mustela vison. Anim. Behav. 77, 349–355. (doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2008.09.036) - DOI
-
- Jensen K, Simpson SJ, Nielsen VH, Hunt J, Raubenheimer D, Mayntz D. 2014. Nutrient-specific compensatory feeding in a mammalian carnivore, the mink, Neovison vison. Br. J. Nutr. 112, 1226–1233. (doi:10.1017/S0007114514001664) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eisert R. 2011. Hypercarnivory and the brain: protein requirements of cats reconsidered. J. Comp. Physiol. B 181, 1–17. (doi:10.1007/s00360-010-0528-0) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Felicetti LA, Robbins CT, Shipley LA. 2003. Dietary protein content alters energy expenditure and composition of the mass gain in grizzly bears (Ursus arctos horribilis). Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 76, 256–261. (doi:10.1086/374279) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
