Cross-species Analyses Unravel the Complexity of H3K27me3 and H4K20me3 in the Context of Neural Stem Progenitor Cells
- PMID: 27429906
- PMCID: PMC4941106
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nepig.2016.04.001
Cross-species Analyses Unravel the Complexity of H3K27me3 and H4K20me3 in the Context of Neural Stem Progenitor Cells
Abstract
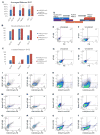
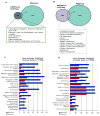
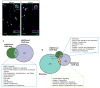
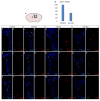
Neural stem progenitor cells (NSPCs) in the human subventricular zone (SVZ) potentially contribute to life-long neurogenesis, yet subtypes of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) contain NSPC signatures that highlight the importance of cell fate regulation. Among numerous regulatory mechanisms, the post-translational methylations onto histone tails are crucial regulator of cell fate. The work presented here focuses on the role of two repressive chromatin marks tri-methylations on histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3) and histone H4 lysine 20 (H4K20me3) in the adult NSPC within the SVZ. To best model healthy human NSPCs as they exist in vivo for epigenetic profiling of H3K27me3 and H4K20me3, we utilized NSPCs isolated from the adult SVZ of baboon brain (Papio anubis) with brain structure and genomic level similar to human. The putative role of H3K27me3 in normal NSPCs predominantly falls into the regulation of gene expression, cell cycle, and differentiation, whereas H4K20me3 is involved in DNA replication/repair, metabolism, and cell cycle. Using conditional knock-out mouse models to diminish Ezh2 and Suv4-20h responsible for H3K27me3 and H4K20me3, respectively, we found that both repressive marks have irrefutable function for cell cycle regulation in the NSPC population. While both EZH2/H3K27me3 and Suv4-20h/H4K20me3 have implication in cancers, our comparative genomics approach between healthy NSPCs and human GBM specimens revealed that substantial sets of genes enriched with H3K27me3 and H4K20me3 in the NSPCs are altered in the human GBM. In sum, our integrated analyses across species highlight important roles of H3K27me3 and H4K20me3 in normal and disease conditions in the context of NSPC.
Keywords: Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP); Cre recombinant protein; Enhancer of zeste (Human- Gene: EZH2, Protein: EZH2) (Mouse- Gene: Ezh2, Protein: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2); Epigenetic Repression; Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM); Neural Stem Progenitor Cells (NSPCs); Stereotaxic injection; Suppressor of variegation homolog 1 (Human- Gene: KMT5B or SUV420H1, Protein: lysine methyltransferase 5B, synonym Suv4-20h1) (Mouse- Gene: Suv4-20h1, synonym Kmt5b, Protein: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase KMT5B, synonym Suv4-20h1); Suppressor of variegation homolog 2 (Human- Gene: KMT5C or SUV420H2, Protein: lysine methyltransferase 5C, synonym Suv4-20h2) (Mouse- Gene: Suv4-20h2, synonym Kmt5c, Protein: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase KMT5C, synonym Suv4-20h2); tri-methylation at histone 3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3) and histone 4 lysine 20 (H4K20me3)..
Figures



References
-
- Trievel RC, Beach BM, Dirk LM, Houtz RL, Hurley JH. Structure and catalytic mechanism of a SET domain protein methyltransferase. Cell. 2002;111:91–103. - PubMed
-
- Varambally S, Dhanasekaran SM, Zhou M, Barrette TR, Kumar-Sinha C, Sanda MG, Ghosh D, Pienta KJ, Sewalt RG, Otte AP, et al. The polycomb group protein EZH2 is involved in progression of prostate cancer. Nature. 2002;419:624–629. - PubMed
-
- Kleer CG, Cao Q, Varambally S, Shen R, Ota I, Tomlins SA, Ghosh D, Sewalt RG, Otte AP, Hayes DF, et al. EZH2 is a marker of aggressive breast cancer and promotes neoplastic transformation of breast epithelial cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2003;100:11606–11611. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ting AH, McGarvey KM, Baylin SB. The cancer epigenome--components and functional correlates. Genes & development. 2006;20:3215–3231. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
