"Lupoid hepatitis" in SLE patients and mice with experimental lupus
- PMID: 27430519
- PMCID: PMC5159230
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.07.007
"Lupoid hepatitis" in SLE patients and mice with experimental lupus
Abstract
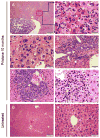
The unusual subset of patients with severe hepatitis, hypergammaglobulinemia, arthritis, and LE cells in the blood reported by Henry Kunkel and others suggested to these investigators that "lupoid" hepatitis might share pathogenic mechanisms with SLE. More than half a century later, the etiology of autoimmune hepatitis remains unclear. The occurrence of autoimmune hepatitis in a small fraction (about 3%) of SLE patients in our lupus cohort and in two mouse models of SLE supports their conclusion that lupoid hepatitis may be share pathogenic mechanisms with SLE. The development of autoimmune hepatitis in mice with pristane-induced lupus provides an opportunity to further explore the potential link between these two autoimmune disorders.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Study on experimental systemic lupus erythematosus mouse model induced by pristane].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Feb;27(2):119-22. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21315035 Chinese.
-
[A case of anti-LKM 1 positive autoimmune hepatitis accompanied by systemic lupus erythematosus].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008 Mar;51(3):190-3. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18451693 Korean.
-
The potential protective role of hepatitis B virus infection in pristane-induced lupus in mice.Lupus. 2016 Oct;25(11):1180-9. doi: 10.1177/0961203316631637. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Lupus. 2016. PMID: 27125291
-
Pristane-induced lupus: considerations on this experimental model.Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Nov;36(11):2403-2414. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3811-6. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28879482 Review.
-
Association of autoimmune hepatitis and systemic lupus erythematodes: a case series and review of the literature.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 21;20(35):12662-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12662. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25253972 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Hepatic Deposited Immunoglobulin G in the Pathogenesis of Liver Damage in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 25;9:1457. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01457. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29988500 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibodies associated with primary biliary cholangitis are common among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus even in the absence of elevated liver enzymes.Clin Exp Immunol. 2021 Jan;203(1):22-31. doi: 10.1111/cei.13512. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32910463 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Galectin-3 orchestrates the histology of mesentery and protects liver during lupus-like syndrome induced by pristane.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 10;9(1):14620. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50564-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31601823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bearn AG, Kunkel HG, Slater RJ. The problem of chronic liver disease in young women. AmJMed. 1956;21:3–15. - PubMed
-
- Mackay IR. A 50-year experience with autoimmune hepatitis: and where are we now? JGastroenterol. 2011;46(Suppl 1):17–28. - PubMed
-
- Sahebjam F, Vierling JM. Autoimmune hepatitis. FrontMed. 2015;9(2):187–219. - PubMed
-
- Homberg JC, Abuaf N, Bernard O, Islam S, Alvarez F, Khalil SH, et al. Chronic active hepatitis associated with antiliver/kidney microsome antibody type 1: a second type of “autoimmune” hepatitis. Hepatology. 1987;7(6):1333–9. - PubMed
-
- Krawitt EL. Discrimination of autoimmune hepatitis: autoantibody typing and beyond. JGastroenterol. 2011;46(Suppl 1):39–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

