The neutrophil elastase inhibitor, sivelestat, attenuates sepsis-related kidney injury in rats
- PMID: 27430552
- PMCID: PMC4990314
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2665
The neutrophil elastase inhibitor, sivelestat, attenuates sepsis-related kidney injury in rats
Abstract
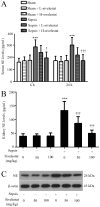
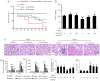
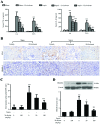
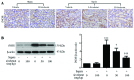
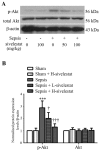
Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) represents a major cause of mortality in intensive care units. Sivelestat, a selective inhibitor of neutrophil elastase (NE), can attenuate sepsis-related acute lung injury. However, whether sivelestat can preserve kidney function during sepsis remains unclear. In this study, we thus examined the effects of sivelestat on sepsis-related AKI. Cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) was performed to induce multiple bacterial infection in male Sprague-Dawley rats, and subsequently, 50 or 100 mg/kg sivelestat were administered by intraperitoneal injection immediately after the surgical procedure. In the untreated rats with sepsis, the mean arterial pressure (MAP) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) were decreased, whereas serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) levels were increased. We found that sivelestat promoted the survival of the rats with sepsis, restored the impairment of MAP and GFR, and inhibited the increased BUN and NGAL levels; specifically, the higher dose was more effective. In addition, sivelestat suppressed the CLP-induced macrophage infiltration, the overproduction of pro-inflammatory mediators (tumor necrosis factor‑α, interleukin-1β, high-mobility group box 1 and inducible nitric oxide synthase) and serine/threonine kinase (Akt) pathway activation in the rats. Collectively, our data suggest that the inhibition of NE activity with the inhibitor, sivelestat, is beneficial in ameliorating sepsis-related kidney injury.
Figures
References
-
- Fry DE. Sepsis, systemic inflammatory response, and multiple organ dysfunction: the mystery continues. Am Surg. 2012;78:1–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

