Pathways to emotional closeness in neonatal units - a cross-national qualitative study
- PMID: 27430590
- PMCID: PMC4949764
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-016-0955-3
Pathways to emotional closeness in neonatal units - a cross-national qualitative study
Abstract
Background: Research shows evidence for the importance of physical and emotional closeness for the infant, the parent and the infant-parent dyad. Less is known about how, when and why parents experience emotional closeness to their infants in a neonatal unit (NU), which was the aim of this study.
Methods: A qualitative study using a salutogenic approach to focus on positive health and wellbeing was undertaken in three NUs: one in Sweden, England and Finland. An 'emotional closeness' form was devised, which asked parents to describe moments/situations when, how and why they had felt emotionally close to their infant. Data for 23 parents of preterm infants were analyzed using thematic networks analysis.
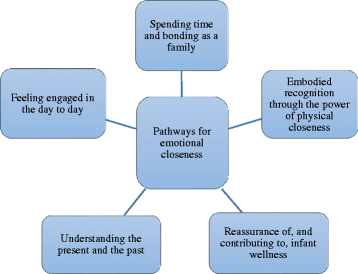
Results: A global theme of 'pathways for emotional closeness' emerged from the data set. This concept related to how emotional, physical, cognitive and social influences led to feelings of emotional closeness between parents and their infants. The five underpinning organising themes relate to the: Embodied recognition through the power of physical closeness; Reassurance of, and contributing to, infant wellness; Understanding the present and the past; Feeling engaged in the day to day and Spending time and bonding as a family.
Conclusion: These findings generate important insights into why, how and when parents feel emotionally close. This knowledge contributes to an increased awareness of how to support parents of premature infants to form positive and loving relationships with their infants. Health care staff should create a climate where parents' emotions and their emotional journey are individually supported.
Keywords: Closeness; Emotion; Infant; Neonatal; Parents; Thematic analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Montirosso R, Fedeli C, Del Prete A, Calciolari G, Borgatti R, Group N-AS. Maternal stress and depressive symptoms associated with quality of developmental care in 25 Italian Neonatal Intensive Care Units: a cross sectional observational study. Int J Nurs Stud. 2014;51(7):994–1002. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2013.11.001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous