"Delirium Day": a nationwide point prevalence study of delirium in older hospitalized patients using an easy standardized diagnostic tool
- PMID: 27430902
- PMCID: PMC4950237
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-016-0649-8
"Delirium Day": a nationwide point prevalence study of delirium in older hospitalized patients using an easy standardized diagnostic tool
Abstract
Background: To date, delirium prevalence in adult acute hospital populations has been estimated generally from pooled findings of single-center studies and/or among specific patient populations. Furthermore, the number of participants in these studies has not exceeded a few hundred. To overcome these limitations, we have determined, in a multicenter study, the prevalence of delirium over a single day among a large population of patients admitted to acute and rehabilitation hospital wards in Italy.
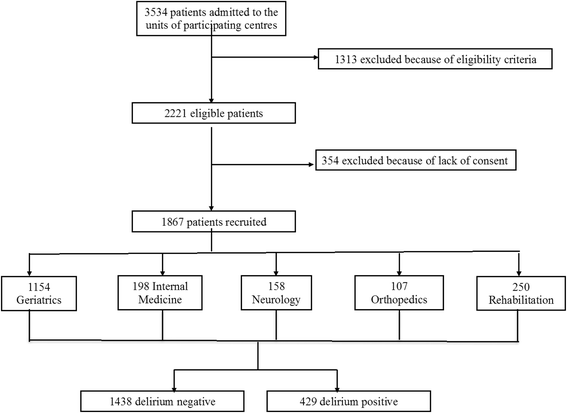
Methods: This is a point prevalence study (called "Delirium Day") including 1867 older patients (aged 65 years or more) across 108 acute and 12 rehabilitation wards in Italian hospitals. Delirium was assessed on the same day in all patients using the 4AT, a validated and briefly administered tool which does not require training. We also collected data regarding motoric subtypes of delirium, functional and nutritional status, dementia, comorbidity, medications, feeding tubes, peripheral venous and urinary catheters, and physical restraints.
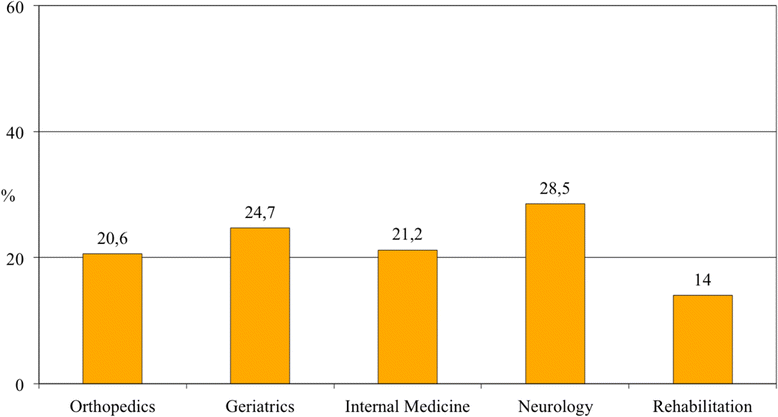
Results: The mean sample age was 82.0 ± 7.5 years (58 % female). Overall, 429 patients (22.9 %) had delirium. Hypoactive was the commonest subtype (132/344 patients, 38.5 %), followed by mixed, hyperactive, and nonmotoric delirium. The prevalence was highest in Neurology (28.5 %) and Geriatrics (24.7 %), lowest in Rehabilitation (14.0 %), and intermediate in Orthopedic (20.6 %) and Internal Medicine wards (21.4 %). In a multivariable logistic regression, age (odds ratio [OR] 1.03, 95 % confidence interval [CI] 1.01-1.05), Activities of Daily Living dependence (OR 1.19, 95 % CI 1.12-1.27), dementia (OR 3.25, 95 % CI 2.41-4.38), malnutrition (OR 2.01, 95 % CI 1.29-3.14), and use of antipsychotics (OR 2.03, 95 % CI 1.45-2.82), feeding tubes (OR 2.51, 95 % CI 1.11-5.66), peripheral venous catheters (OR 1.41, 95 % CI 1.06-1.87), urinary catheters (OR 1.73, 95 % CI 1.30-2.29), and physical restraints (OR 1.84, 95 % CI 1.40-2.40) were associated with delirium. Admission to Neurology wards was also associated with delirium (OR 2.00, 95 % CI 1.29-3.14), while admission to other settings was not.
Conclusions: Delirium occurred in more than one out of five patients in acute and rehabilitation hospital wards. Prevalence was highest in Neurology and lowest in Rehabilitation divisions. The "Delirium Day" project might become a useful method to assess delirium across hospital settings and a benchmarking platform for future surveys.
Keywords: 4AT; Delirium; Hospital; Multicenter; Prevalence.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
-
- Davis DH, Skelly DT, Murray C, Hennessy E, Bowen J, Norton S, Brayne C, Rahkonen T, Sulkava R, Sanderson DJ, Rawlins JN, Bannerman DM, MacLullich AMJ, Cunningham C.. Worsening cognitive impairment and neurodegenerative pathology progressively increase risk for delirium. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2015;23:403–15. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellelli G, Mazzola P, Morandi A, Bruni A, Carnevali L, Corsi M, Zatti G, Zambon A, Corrao G, Olofsson B, Gustafson Y, Annoni G. Duration of postoperative delirium is an independent predictor of 6-month mortality in older adults after hip fracture. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62:1335–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical