Protection of rat liver against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by a novel selenocysteine-containing 7-mer peptide
- PMID: 27431272
- PMCID: PMC4991737
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5464
Protection of rat liver against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by a novel selenocysteine-containing 7-mer peptide
Abstract
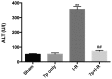
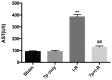
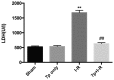
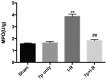
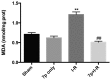
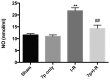
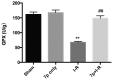
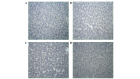
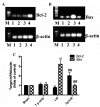
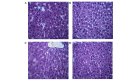
Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion (I-R) injury causes acute organ damage or dysfunction, and remains a problem for liver transplantation. In the I-R phase, the generation of reactive oxygen species aggravates the injury. In the current study, a novel selenocysteine-containing 7‑mer peptide (H-Arg-Sec-Gly-Arg-Asn-Ala-Gln-OH) was constructed to imitate the active site of an antioxidant enzyme, glutathione peroxidase (GPX). The 7‑mer peptide which has a lower molecular weight, and improved water‑solubility, higher stability and improved cell membrane permeability compared with other GPX mimics. Its GPX activity reached 13 U/µmol, which was 13 times that of ebselen (a representative GPX mimic). The effect of this GPX mimic on I‑R injury of the liver was assessed in rats. The 7‑mer peptide significantly inhibited the increase in serum hepatic amino‑transferases, tissue malondialdehyde, nitric oxide contents, myeloperoxidase activity and decrease of GPX activity compared with I‑R tissue. Following treatment with the 7‑mer peptide, the expression of B‑cell CLL/lymphoma‑2 (Bcl‑2) was significantly upregulated at the mRNA and protein level compared with the I‑R group, as determined by reverse transcription‑polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry, respectively. By contrast, Bcl‑2 associated X protein (Bax) was downregulated by the 7‑mer peptide compared the I‑R group. Histological and ultrastructural changes of the rat liver tissue were also compared among the experimental groups. The results of the current study suggest that the 7‑mer peptide protected the liver against hepatic I‑R injury via suppression of oxygen‑derived free radicals and regulation of Bcl‑2 and Bax expression, which are involved in the apoptosis of liver cells. The findings of the present study will further the investigation of the 7-mer peptide as an effective therapeutic agent in hepatic I-R injury.
Figures



References
-
- Taki-Eldin A, Zhou L, Xie HY, Chen KJ, Yu D, He Y, Zheng SS. Triiodothyronine attenuates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in a partial hepatectomy model through inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines, transcription factors, and adhesion molecules. J Surg Res. 2012;178:646–656. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.05.069. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

