Mutant IDH: a targetable driver of leukemic phenotypes linking metabolism, epigenetics and transcriptional regulation
- PMID: 27431380
- PMCID: PMC5066133
- DOI: 10.2217/epi-2016-0008
Mutant IDH: a targetable driver of leukemic phenotypes linking metabolism, epigenetics and transcriptional regulation
Abstract
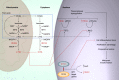
Aberrant epigenomic programming is a hallmark of acute myeloid leukemia. This is partially due to somatic mutations that perturb cytosine methylation, histone post-translational modifications and transcription factors. Remarkably, mutations in the IDH1 and IDH2 genes perturb the epigenome through all three of these mechanisms. Mutant IDH enzymes produce high levels of the oncometabolite (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate that competitively inhibits dioxygenase enzymes that modify methylcytosine to hydroxymethylcytosine and histone tail methylation. The development of IDH mutant specific inhibitors may now enable the therapeutic reprogramming of both layers of the epigenome spontaneously to revert the malignant phenotype of these leukemias and improve clinical outcome for acute myeloid leukemia patients with IDH mutations.
Keywords: AML; DNA methylation; IDH; epigenomics; histone tail methylation; hydroxymethylcytosine; leukemogenesis; mutation; targeted therapy; transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial & competing interests disclosure The authors wish to thank the following sources of financial support: NCI R01CA198089 to AM Melnick, NCI K08CA169055 and funding from the American Society of Hematology (ASHAMFDP-20121) under the ASH-AMFDP partnership with The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation to FEG Bakelman. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Meyer SC, Levine RL. Translational implications of somatic genomics in acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(9):e382–e394. - PubMed
-
- Wang ZY, Chen Z. Acute promyelocytic leukemia: from highly fatal to highly curable. Blood. 2008;111(5):2505–2515. - PubMed
-
- Stone RM, Mandrekar S, Sanford BL, et al. The multi-kinase inhibitor midostaurin (M) prolongs survival compared with placebo (P) in combination with daunorubicin (D)/cytarabine (C) induction (ind), high-dose C consolidation (consol), and as maintenance (maint) therapy in newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients (pts) age 18–60 with FLT3 mutations (muts): an international prospective randomized (rand) P-controlled double-blind trial (CALGB 10603/RATIFY [Alliance]) Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2015;126(23):6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
