Response rates and durability of chemotherapy among 62 patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma
- PMID: 27431483
- PMCID: PMC5055152
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.815
Response rates and durability of chemotherapy among 62 patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma
Abstract
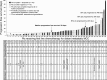
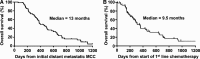
Cytotoxic chemotherapy is commonly used to treat advanced Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). However, its efficacy in distant metastatic MCC patients is unclear, in part because most prior reports aggregated these patients with those receiving adjuvant chemotherapy and combined chemoradiation for whom prognosis and outcomes may differ. In this retrospective study, we analyzed detailed records from 62 patients with distant metastatic MCC treated with cytotoxic chemotherapy. Efficacy outcomes including response rate (RR), durability of response (DOR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) were evaluated. In this cohort, platinum plus etoposide was the most commonly used first-line regimen (69%). RR to first-line chemotherapy was 55% (34/62) with complete responses (CR) in 13% (8/62) and partial responses (PR) in 42% (26/62) while 6% (4/62) had stable disease and 39% (24/62) had progressive disease. Median PFS was 94 days and median OS was 9.5 months from start of chemotherapy. Among responding patients (n = 34), median PFS was 168 days and median DOR was 85 days. Among 30 of the 62 patients who received second-line chemotherapy, RR was 23% (7/30; 1 CR, 6 PR), median PFS was 61 days, and median DOR was 101 days. In summary, first-line chemotherapy is associated with a high RR in metastatic MCC, but responses are typically not durable, and the median PFS is only 3 months. These results suggest rapid emergence of chemoresistance in MCC tumors, and may serve as a useful comparator for immunotherapies currently being explored for metastatic MCC.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Merkel cell carcinoma; durability of response; metastatic; neuroendocrine tumor; progression-free survival; response rate.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

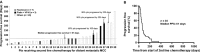
Similar articles
-
Real-world treatment outcomes in patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma treated with chemotherapy in the USA.Future Oncol. 2017 Aug;13(19):1699-1710. doi: 10.2217/fon-2017-0187. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Future Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28605939
-
Three-year survival, correlates and salvage therapies in patients receiving first-line pembrolizumab for advanced Merkel cell carcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Apr;9(4):e002478. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002478. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33879601 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Updated efficacy of avelumab in patients with previously treated metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma after ≥1 year of follow-up: JAVELIN Merkel 200, a phase 2 clinical trial.J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Jan 19;6(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40425-017-0310-x. J Immunother Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29347993 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chemotherapy in neuroendocrine/Merkel cell carcinoma of the skin: case series and review of 204 cases.J Clin Oncol. 2000 Jun;18(12):2493-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2000.18.12.2493. J Clin Oncol. 2000. PMID: 10856110 Review.
-
Merkel cell carcinoma: report of 10 cases and review of the literature.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Nov;43(5 Pt 1):755-67. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2000.106505. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000. PMID: 11050578 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Combined Anti-programmed Death-ligand 1 Therapy and Radiotherapy for Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Two Case Reports.Acta Derm Venereol. 2020 Aug 18;100(15):adv00237. doi: 10.2340/00015555-3593. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020. PMID: 32720697 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Large T Antigen in the Molecular Pathogenesis of Merkel Cell Carcinoma.Genes (Basel). 2024 Aug 27;15(9):1127. doi: 10.3390/genes15091127. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypercalcaemia due to Sarcoidosis during Treatment with Avelumab for Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma.Case Rep Oncol. 2019 Aug 8;12(2):639-643. doi: 10.1159/000502285. eCollection 2019 May-Aug. Case Rep Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31543781 Free PMC article.
-
Driving innovation for rare skin cancers: utilizing common tumours and machine learning to predict immune checkpoint inhibitor response.Immunooncol Technol. 2019 Nov 27;4:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.iotech.2019.11.002. eCollection 2019 Dec. Immunooncol Technol. 2019. PMID: 35755000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early objective response to avelumab treatment is associated with improved overall survival in patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019 Apr;68(4):609-618. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-02295-4. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30721341 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Allen, P. J. , Bowne W. B., Jaques D. P., Brennan M. F., Busam K., and Coit D. G.. 2005. Merkel cell carcinoma: prognosis and treatment of patients from a single institution. J. Clin. Oncol. 23:2300–2309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

