Echinacoside Protects Against MPP(+)-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis via ROS/ATF3/CHOP Pathway Regulation
- PMID: 27432061
- PMCID: PMC5563786
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-016-0047-4
Echinacoside Protects Against MPP(+)-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis via ROS/ATF3/CHOP Pathway Regulation
Abstract
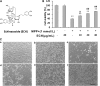
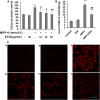
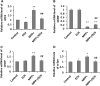
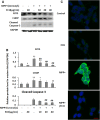
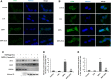
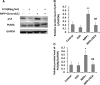
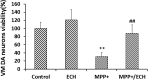
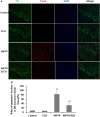
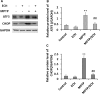
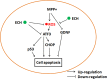
Echinacoside (ECH) is protective in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease (PD) induced by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP(+)). To investigate the mechanisms involved, SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells were treated with MPP(+) or a combination of MPP(+) and ECH, and the expression of ATF3 (activating transcription factor 3), CHOP (C/EBP-homologous protein), SCNA (synuclein alpha), and GDNF (glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor) was assessed. The results showed that ECH significantly improved cell survival by inhibiting the generation of MPP(+)-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS). In addition, ECH suppressed the ROS and MPP(+)-induced expression of apoptotic genes (ATF3, CHOP, and SCNA). ECH markedly decreased the MPP(+)-induced caspase-3 activity in a dose-dependent manner. ATF3-knockdown also decreased the CHOP and cleaved caspase-3 levels and inhibited the apoptosis induced by MPP(+). Interestingly, ECH partially restored the GDNF expression that was down-regulated by MPP(+). ECH also improved dopaminergic neuron survival during MPP(+) treatment and protected these neurons against the apoptosis induced by MPTP. Taken together, these data suggest that the ROS/ATF3/CHOP pathway plays a critical role in mechanisms by which ECH protects against MPP(+)-induced apoptosis in PD.
Keywords: 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion; ATF3; CHOP; Echinacoside; Parkinson’s disease; Reactive oxygen species.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Echinacoside, an Inestimable Natural Product in Treatment of Neurological and other Disorders.Molecules. 2018 May 18;23(5):1213. doi: 10.3390/molecules23051213. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29783690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synphilin-1 has neuroprotective effects on MPP+-induced Parkinson's disease model cells by inhibiting ROS production and apoptosis.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Jan 18;690:145-150. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.10.020. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 30316984
-
Secalonic acid A protects dopaminergic neurons from 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP⁺)-induced cell death via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug 5;713(1-3):58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.04.029. Epub 2013 May 9. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23665112
-
Echinacoside protects dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β signaling pathway in MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease model.Brain Res Bull. 2020 Nov;164:55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.08.015. Epub 2020 Aug 23. Brain Res Bull. 2020. PMID: 32846198
-
MiR-212 Attenuates MPP⁺-Induced Neuronal Damage by Targeting KLF4 in SH-SY5Y Cells.Yonsei Med J. 2018 May;59(3):416-424. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.3.416. Yonsei Med J. 2018. PMID: 29611404 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Echinacoside, an Inestimable Natural Product in Treatment of Neurological and other Disorders.Molecules. 2018 May 18;23(5):1213. doi: 10.3390/molecules23051213. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29783690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Echinacoside on Regulating the Stress-Active p38MAPK and NF-κB p52 Signals in the Mice Model of Parkinson's Disease.Neurochem Res. 2017 Apr;42(4):975-985. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2130-7. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 27981472
-
ASC-J9® suppresses prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion via altering the ATF3-PTK2 signaling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 4;40(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01760-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33390173 Free PMC article.
-
Further structure-activity relationships study of substituted dithiolethiones as glutathione-inducing neuroprotective agents.Chem Cent J. 2016 Oct 19;10:64. doi: 10.1186/s13065-016-0210-z. eCollection 2016. Chem Cent J. 2016. PMID: 27812368 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Amyloid Beta Aggregation and Deposition of Cistanche tubulosa Aqueous Extract.Molecules. 2019 Feb 14;24(4):687. doi: 10.3390/molecules24040687. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30769881 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

