α-TEA inhibits the growth and motility of human colon cancer cells via targeting RhoA/ROCK signaling
- PMID: 27432222
- PMCID: PMC4991732
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5525
α-TEA inhibits the growth and motility of human colon cancer cells via targeting RhoA/ROCK signaling
Abstract
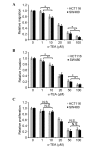
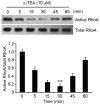
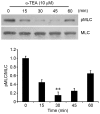
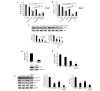
Colon or colorectal cancer is a common type of human cancer, which originates in the intestine crassum or the rectum. In the United States, colorectal cancer has one of the highest rates of cancer‑related mortality. Investigating novel chemotherapeutic approaches is significant in the treatment of cancers, such as colorectal cancer. α-tocopherol ether-linked acetic acid (α-TEA) is a potent anticancer agent in multiple types of human cancer. However, its effect remains to be determined in colon cancer. In this study, HCT116 and SW480 human colon cancer cells were used to investigate the anticancer role of α-TEA. It was demonstrated that α-TEA inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion in colon cancer cells. Furthermore, it was shown that α-TEA downregulated the activity of RhoA and phosphorylated Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) substrate myosin light chain (MLC) using a pull-down assay and western blotting, respectively, implying that the RhoA/ROCK pathway is involved in α-TEA-mediated cell growth and motility inhibition. In order to confirm this hypothesis a RhoA inhibitor (clostridium botulinum C3 exoenzyme), a ROCK inhibitor (Y27632) and RhoA small interfering (si)RNA were applied to block RhoA/ROCK signaling. This resulted in the attenuation of MLC phosphorylation, and augmentation of α-TEA-mediated growth and motility inhibition in colon cancer cells. In conclusion, these results indicate that α-TEA inhibits growth and motility in colon cancer cells possibly by targeting RhoA/ROCK signaling. Moreover, combined with RhoA or ROCK inhibitors, α-TEA may exhibit a more effective inhibitory role in colon cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vincristine promotes migration and invasion of colorectal cancer HCT116 cells through RhoA/ROCK/ Myosin light chain pathway.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016 Oct 31;62(12):91-96. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2016.62.12.16. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016. PMID: 27894406
-
MiR-31 Regulates Rho-Associated Kinase-Myosin Light Chain (ROCK-MLC) Pathway and Inhibits Gastric Cancer Invasion: Roles of RhoA.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Dec 1;22:4679-4691. doi: 10.12659/msm.898399. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27904131 Free PMC article.
-
Vincristine enhances amoeboid-like motility via GEF-H1/RhoA/ROCK/Myosin light chain signaling in MKN45 cells.BMC Cancer. 2012 Oct 12;12:469. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-469. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23057787 Free PMC article.
-
Role of RhoA-ROCK signaling inhibitor fasudil in Alzheimer disease.Behav Brain Res. 2025 Apr 27;484:115524. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2025.115524. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40043855 Review.
-
Pathophysiological effects of RhoA and Rho-associated kinase on cardiovascular system.J Hypertens. 2016 Jan;34(1):3-10. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000768. J Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26556565 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of α-tocopheryloxy acetic acid, a vitamin E derivative mitocan, on the experimental infection of mice with Plasmodium yoelii.Malar J. 2021 Jun 24;20(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12936-021-03817-9. Malar J. 2021. PMID: 34167535 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of α-Tocopheryloxy Acetic Acid on the Infection of Mice with Plasmodium berghei ANKA In Vivo and Humans with P. falciparum In Vitro.Acta Parasitol. 2022 Dec;67(4):1514-1520. doi: 10.1007/s11686-022-00604-7. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Acta Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35951222
-
Effects of isoprenylcysteine carboxyl methyltransferase silencing on the proliferation and apoptosis of tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Feb 1;39(1):64-73. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2021.01.010. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33723939 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Dietary patterns in association with the expression of pro-metastatic genes in primary breast cancer.Eur J Nutr. 2022 Sep;61(6):3267-3284. doi: 10.1007/s00394-022-02884-1. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Eur J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35484415
-
Procaine Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Colon Cancer Cells Through Inactivation of the ERK/MAPK/FAK Pathways by Regulation of RhoA.Oncol Res. 2018 Mar 5;26(2):209-217. doi: 10.3727/096504017X14944585873622. Epub 2017 May 11. Oncol Res. 2018. Retraction in: Oncol Res. 2025 Mar 19;33(4):991. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.056914. PMID: 28492141 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures 2014. American Cancer Society; Atlanta: 2014.
-
- Colon cancer Healthy women. http://www.healthywomen.org/condition/colon-cancer. Accessed July 8, 2016.
-
- Anderson K, Lawson KA, Simmons-Menchaca M, Sun L, Sanders BG, Kline K. Alpha-TEA plus cisplatin reduces human cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell tumor burden and metastasis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2004;229:1169–1176. - PubMed
-
- Lawson KA, Anderson K, Simmons-Menchaca M, Atkinson J, Sun L, Sanders BG, Kline K. Comparison of vitamin E derivatives α-TEA and VES in reduction of mouse mammary tumor burden and metastasis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2004;229:954–963. - PubMed
-
- Shun MC, Yu W, Gapor A, Parsons R, Atkinson J, Sanders BG, Kline K. Pro-apoptotic mechanisms of action of a novel vitamin E analog (alpha-TEA) and a naturally occurring form of vitamin E (delta-tocotrienol) in MDA-MB-435 human breast cancer cells. Nutr Cancer. 2004;48:95–105. doi: 10.1207/s15327914nc4801_13. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

