Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer
- PMID: 27432227
- PMCID: PMC5050111
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0596
Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer
Abstract
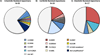
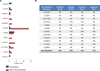
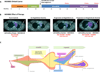
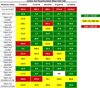
Advanced, anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive lung cancer is currently treated with the first-generation ALK inhibitor crizotinib followed by more potent, second-generation ALK inhibitors (e.g., ceritinib and alectinib) upon progression. Second-generation inhibitors are generally effective even in the absence of crizotinib-resistant ALK mutations, likely reflecting incomplete inhibition of ALK by crizotinib in many cases. Herein, we analyzed 103 repeat biopsies from ALK-positive patients progressing on various ALK inhibitors. We find that each ALK inhibitor is associated with a distinct spectrum of ALK resistance mutations and that the frequency of one mutation, ALKG1202R, increases significantly after treatment with second-generation agents. To investigate strategies to overcome resistance to second-generation ALK inhibitors, we examine the activity of the third-generation ALK inhibitor lorlatinib in a series of ceritinib-resistant, patient-derived cell lines, and observe that the presence of ALK resistance mutations is highly predictive for sensitivity to lorlatinib, whereas those cell lines without ALK mutations are resistant.
Significance: Secondary ALK mutations are a common resistance mechanism to second-generation ALK inhibitors and predict for sensitivity to the third-generation ALK inhibitor lorlatinib. These findings highlight the importance of repeat biopsies and genotyping following disease progression on targeted therapies, particularly second-generation ALK inhibitors. Cancer Discov; 6(10); 1118-33. ©2016 AACRSee related commentary by Qiao and Lovly, p. 1084This article is highlighted in the In This Issue feature, p. 1069.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


Comment in
-
Cracking the Code of Resistance across Multiple Lines of ALK Inhibitor Therapy in Lung Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2016 Oct;6(10):1084-1086. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0910. Cancer Discov. 2016. PMID: 27698100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa K, Mekhail T, et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2167–2177. - PubMed
-
- Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, Seto T, Crino L, Ahn MJ, et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2385–2394. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

