The impact of patient navigation on the delivery of diagnostic breast cancer care in the National Patient Navigation Research Program: a prospective meta-analysis
- PMID: 27432417
- PMCID: PMC5216421
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-016-3887-8
The impact of patient navigation on the delivery of diagnostic breast cancer care in the National Patient Navigation Research Program: a prospective meta-analysis
Abstract
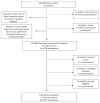
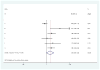
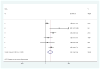
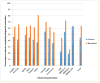
Patient navigation is emerging as a standard in breast cancer care delivery, yet multi-site data on the impact of navigation at reducing delays along the continuum of care are lacking. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of navigation on reaching diagnostic resolution at specific time points after an abnormal breast cancer screening test among a national sample. A prospective meta-analysis estimated the adjusted odds of achieving timely diagnostic resolution at 60, 180, and 365 days. Exploratory analyses were conducted on the pooled sample to identify which groups had the most benefit from navigation. Clinics from six medical centers serving vulnerable populations participated in the Patient Navigation Research Program. Women with an abnormal breast cancer screening test between 2007 and 2009 were included and received the patient navigation intervention or usual care. Patient navigators worked with patients and their care providers to address patient-specific barriers to care to prevent delays in diagnosis. A total of 4675 participants included predominantly racial/ethnic minorities (74 %) with public insurance (40 %) or no insurance (31 %). At 60 days and 180 days, there was no statistically significant effect of navigation on achieving timely diagnostic care, but a benefit of navigation was seen at 365 days (aOR 2.12, CI 1.36-3.29). We found an equal benefit of navigation across all groups, regardless of race/ethnicity, language, insurance status, and type of screening abnormality. Patient navigation resulted in more timely diagnostic resolution at 365 days among a diverse group of minority, low-income women with breast cancer screening abnormalities. Trial registrations clinicaltrials.gov Identifiers: NCT00613275, NCT00496678, NCT00375024, NCT01569672.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Care delivery; Disparities; Patient navigation.
Figures

References
-
- Hunt BR, Whitman S, Hurlbert MS. Increasing black: white disparities in breast cancer mortality in the 50 largest cities in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol. 2014;38:118–123. - PubMed
-
- Bayraktar UD, Chen E, Bayraktar S, et al. Does delay of adjuvant chemotherapy impact survival in patients with resected stage II and III colon adenocarcinoma? Cancer. 2011;117:2364–2370. - PubMed
-
- Brawley OW. Some perspective on black-white cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2002;52:322–325. - PubMed
-
- Fedewa SA, Ward EM, Stewart AK, Edge SB. Delays in adjuvant chemotherapy treatment among patients with breast cancer are more likely in African American and Hispanic populations: a national cohort study 2004–2006. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4135–4141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 CA116875/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA116892/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA116937/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA117281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA203000/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA116885/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA116903/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA116924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA202995/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA202997/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA116925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

