Rifampin Resistance rpoB Alleles or Multicopy Thioredoxin/Thioredoxin Reductase Suppresses the Lethality of Disruption of the Global Stress Regulator spx in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 27432833
- PMCID: PMC5019056
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00261-16
Rifampin Resistance rpoB Alleles or Multicopy Thioredoxin/Thioredoxin Reductase Suppresses the Lethality of Disruption of the Global Stress Regulator spx in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
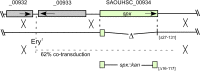
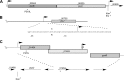
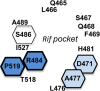
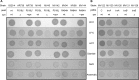
Staphylococcus aureus is capable of causing a remarkable spectrum of disease, ranging from mild skin eruptions to life-threatening infections. The survival and pathogenic potential of S. aureus depend partly on its ability to sense and respond to changes in its environment. Spx is a thiol/oxidative stress sensor that interacts with the C-terminal domain of the RNA polymerase RpoA subunit, leading to changes in gene expression that help sustain viability under various conditions. Using genetic and deep-sequencing methods, we show that spx is essential in S. aureus and that a previously reported Δspx strain harbored suppressor mutations that allowed it to grow without spx One of these mutations is a single missense mutation in rpoB (a P-to-L change at position 519 encoded by rpoB [rpoB-P519L]) that conferred high-level resistance to rifampin. This mutation alone was found to be sufficient to bypass the requirement for spx The generation of rifampin resistance libraries led to the discovery of an additional rpoB mutation, R484H, which supported strains with the spx disruption. Other rifampin resistance mutations either failed to support the Δspx mutant or were recovered at unexpectedly low frequencies in genetic transduction experiments. The amino acid residues encoded by rpoB-P519L and -R484H map in close spatial proximity and comprise a highly conserved region of RpoB. We also discovered that multicopy expression of either trxA (encoding thioredoxin) or trxB (encoding thioredoxin reductase) supports strains with the deletion of spx Our results reveal intriguing properties, especially of RNA polymerase, that compensate for the loss of an essential gene that is a key mediator of diverse processes in S. aureus, including redox and thiol homeostasis, antibiotic resistance, growth, and metabolism.
Importance: The survival and pathogenicity of S. aureus depend on complex genetic programs. An objective for combating this insidious organism entails dissecting genetic regulatory circuits and discovering promising new targets for therapeutic intervention. In this study, we discovered that Spx, an RNA polymerase-interacting stress regulator implicated in many stress responses in S. aureus, including responses to oxidative and cell wall antibiotics, is essential. We describe two mechanisms that suppress the lethality of spx disruption. One mechanism highlights how only certain rifampin resistance-encoding alleles of RpoB confer new properties on RNA polymerase, with important mechanistic implications. We describe additional stress conditions where the loss of spx is deleterious, thereby highlighting Spx as a multifaceted regulator and attractive drug discovery target.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Redox-sensitive transcriptional control by a thiol/disulphide switch in the global regulator, Spx.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Jan;55(2):498-510. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04395.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15659166
-
Spx-dependent global transcriptional control is induced by thiol-specific oxidative stress in Bacillus subtilis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Nov 11;100(23):13603-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2235180100. Epub 2003 Nov 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14597697 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Amino Acid Residue Requirements of the RNA Polymerase (RNAP) α Subunit C-Terminal Domain for Productive Interaction between Spx and RNAP of Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2017 Jun 27;199(14):e00124-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00124-17. Print 2017 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28484046 Free PMC article.
-
Rifampicin-resistance, rpoB polymorphism and RNA polymerase genetic engineering.J Biotechnol. 2015 May 20;202:60-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.11.024. Epub 2014 Dec 3. J Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25481100 Review.
-
The thioredoxin antioxidant system.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Jan;66:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 23899494 Review.
Cited by
-
Thermosensitive PBP2a requires extracellular folding factors PrsA and HtrA1 for Staphylococcus aureus MRSA β-lactam resistance.Commun Biol. 2019 Nov 15;2:417. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0667-0. eCollection 2019. Commun Biol. 2019. PMID: 31754647 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of resistance mechanisms and biological characteristics of rifampicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains selected in vitro.BMC Microbiol. 2019 Sep 18;19(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1573-9. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31533633 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria monocytogenes SpxA1 is a global regulator required to activate genes encoding catalase and heme biosynthesis enzymes for aerobic growth.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Aug;114(2):230-243. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14508. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32255216 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of ArlRS and VraSR in Regulating Ceftaroline Hypersusceptibility in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jul 6;10(7):821. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070821. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356742 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory circuits controlling Spx levels in Streptococcus mutans.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Jul;114(1):109-126. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14499. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32189382 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

