Directed evolution of a sphingomyelin flippase reveals mechanism of substrate backbone discrimination by a P4-ATPase
- PMID: 27432949
- PMCID: PMC4978280
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1525730113
Directed evolution of a sphingomyelin flippase reveals mechanism of substrate backbone discrimination by a P4-ATPase
Abstract
Phospholipid flippases in the type IV P-type ATPase (P4-ATPases) family establish membrane asymmetry and play critical roles in vesicular transport, cell polarity, signal transduction, and neurologic development. All characterized P4-ATPases flip glycerophospholipids across the bilayer to the cytosolic leaflet of the membrane, but how these enzymes distinguish glycerophospholipids from sphingolipids is not known. We used a directed evolution approach to examine the molecular mechanisms through which P4-ATPases discriminate substrate backbone. A mutagenesis screen in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has identified several gain-of-function mutations in the P4-ATPase Dnf1 that facilitate the transport of a novel lipid substrate, sphingomyelin. We found that a highly conserved asparagine (N220) in the first transmembrane segment is a key enforcer of glycerophospholipid selection, and specific substitutions at this site allow transport of sphingomyelin.
Keywords: P4-ATPase; directed evolution; membrane asymmetry; sphingomyelin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
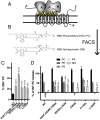
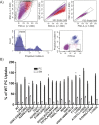

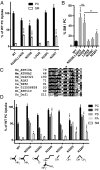
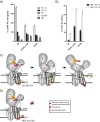


Similar articles
-
Type IV P-type ATPases distinguish mono- versus diacyl phosphatidylserine using a cytofacial exit gate in the membrane domain.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 5;288(27):19516-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.476911. Epub 2013 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23709217 Free PMC article.
-
Two-gate mechanism for phospholipid selection and transport by type IV P-type ATPases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 29;110(5):E358-67. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216948110. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23302692 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast and human P4-ATPases transport glycosphingolipids using conserved structural motifs.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 8;294(6):1794-1806. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005876. Epub 2018 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30530492 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid flippases in polarized growth.Curr Genet. 2021 Apr;67(2):255-262. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01145-0. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33388852 Review.
-
Linking phospholipid flippases to vesicle-mediated protein transport.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jul;1791(7):612-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.03.004. Epub 2009 Mar 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19286470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aminoglycerophospholipid flipping and P4-ATPases in Toxoplasma gondii.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100315. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100315. Epub 2021 Jan 21. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33485966 Free PMC article.
-
Exofacial membrane composition and lipid metabolism regulates plasma membrane P4-ATPase substrate specificity.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 25;295(52):17997-18009. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014794. Epub 2020 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33060204 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of a human plasma membrane phospholipid flippase.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 24;295(30):10180-10194. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014144. Epub 2020 Jun 3. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32493773 Free PMC article.
-
The PQ-loop protein Any1 segregates Drs2 and Neo1 functions required for viability and plasma membrane phospholipid asymmetry.J Lipid Res. 2019 May;60(5):1032-1042. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M093526. Epub 2019 Mar 1. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 30824614 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding P4-ATPase substrate interactions.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Nov/Dec;51(6):513-527. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2016.1237934. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27696908 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vance DE, Vance JE. Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes. 5th Ed Elsevier; Amsterdam: 2008.
-
- Devaux PF, Herrmann A. Transmembrane Dynamics of Lipids. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ: 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

