Hepatopulmonary syndrome: What we know and what we would like to know
- PMID: 27433086
- PMCID: PMC4932208
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i25.5728
Hepatopulmonary syndrome: What we know and what we would like to know
Abstract
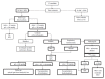
Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) is characterized by abnormalities in blood oxygenation caused by the presence of intrapulmonary vascular dilations (IPVD) in the context of liver disease, generally at a cirrhotic stage. Knowledge about the subject is still only partial. The majority of the information about the etiopathogenesis of HPS has been obtained through experiments on animals. Reported prevalence in patients who are candidates for a liver transplantation (LT) varies between 4% and 32%, with a predominance of mild or moderate cases. Although it is generally asymptomatic it does have an impact on their quality of life and survival. The diagnosis requires taking an arterial blood gas sample of a seated patient with alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient (AaO2) ≥ 15 mm Hg, or ≥ 20 mm Hg in those over 64 years of age. The IPVD are identified through a transthoracic contrast echocardiography or a macroaggregated albumin lung perfusion scan ((99m)Tc-MAA). There is currently no effective medical treatment. LT has been shown to reverse the syndrome and improve survival rates, even in severe cases. Therefore the policy of prioritizing LT would appear to increase survival rates. This paper takes a critical and clinical look at the current understanding of HPS, as well as the controversies surrounding it and possible future research.
Keywords: Contrast echocardiography; Hepatopulmonary syndrome; Liver cirrhosis; Liver transplantation; Macroaggregated albumin lung perfusion scan.
Figures
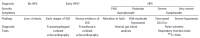
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and characteristics of hepatopulmonary syndrome in children with cirrhosis in southern Brazil.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jan;31(1):10-15. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001207. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30045096
-
The utility of the macro-aggregated albumin lung perfusion scan in the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatopulmonary syndrome in cirrhotic patients candidates for liver transplantation.Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2017 May;109(5):335-343. doi: 10.17235/reed.2017.4219/2016. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2017. PMID: 28301945 Clinical Trial.
-
Technetium-99m-labeled macroaggregated albumin lung perfusion scan for diagnosis of hepatopulmonary syndrome: A prospective study comparing brain uptake and whole-body uptake.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Mar 14;26(10):1088-1097. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i10.1088. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32205999 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatopulmonary syndrome.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Feb;33(1):11-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1301730. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22447256 Review.
-
[Heptopulmonary syndrome].Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Jun-Jul;38(6):398-408. doi: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2015.02.007. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25840463 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Endothelial glycocalyx in hepatopulmonary syndrome: An indispensable player mediating vascular changes.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 22;13:1039618. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1039618. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36618396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First presentation of portal hypertension complicated by hepatopulmonary syndrome.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Sep 20;14(9):e244712. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-244712. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34544713 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Hepatopulmonary Syndrome in a Child with Caroli Syndrome.Case Rep Pediatr. 2017;2017:2171974. doi: 10.1155/2017/2171974. Epub 2017 Aug 13. Case Rep Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28884036 Free PMC article.
-
Development of severe intrapulmonary shunting in a patient with carcinoid heart disease after closure of a persistent foramen ovale: a case report.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2021 Dec 4;5(12):ytab494. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytab494. eCollection 2021 Dec. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 35047738 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatopulmonary syndrome has low prevalence of pulmonary vascular abnormalities on chest computed tomography.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 18;14(10):e0223805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223805. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31626650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodríguez-Roisin R, Krowka MJ, Hervé P, Fallon MB. Pulmonary-Hepatic vascular Disorders (PHD) Eur Respir J. 2004;24:861–880. - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez-Roisin R, Krowka MJ. Hepatopulmonary syndrome--a liver-induced lung vascular disorder. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2378–2387. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy TC, Knudson RJ. Exercise-aggravated hypoxemia and orthodeoxia in cirrhosis. Chest. 1977;72:305–309. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Roisin R, Roca J. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: the paradigm of liver-induced hypoxaemia. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1997;11:387–406. - PubMed
-
- Krowka MJ, Cortese DA. Hepatopulmonary syndrome. Chest. 1990;98:1053–1054. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

