Establishment of a nested-ASP-PCR method to determine the clarithromycin resistance of Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 27433095
- PMCID: PMC4932217
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i25.5822
Establishment of a nested-ASP-PCR method to determine the clarithromycin resistance of Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
Aim: To investigate clarithromycin resistance positions 2142, 2143 and 2144 of the 23SrRNA gene in Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) by nested-allele specific primer-polymerase chain reaction (nested-ASP-PCR).
Methods: The gastric tissue and saliva samples from 99 patients with positive results of the rapid urease test (RUT) were collected. The nested-ASP-PCR method was carried out with the external primers and inner allele-specific primers corresponding to the reference strain and clinical strains. Thirty gastric tissue and saliva samples were tested to determine the sensitivity of nested-ASP-PCR and ASP-PCR methods. Then, clarithromycin resistance was detected for 99 clinical samples by using different methods, including nested-ASP-PCR, bacterial culture and disk diffusion.
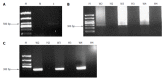
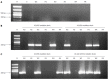
Results: The nested-ASP-PCR method was successfully established to test the resistance mutation points 2142, 2143 and 2144 of the 23SrRNA gene of H. pylori. Among 30 samples of gastric tissue and saliva, the H. pylori detection rate of nested-ASP-PCR was 90% and 83.33%, while the detection rate of ASP-PCR was just 63% and 56.67%. Especially in the saliva samples, nested-ASP-PCR showed much higher sensitivity in H. pylori detection and resistance mutation rates than ASP-PCR. In the 99 RUT-positive gastric tissue and saliva samples, the H. pylori-positive detection rate by nested-ASP-PCR was 87 (87.88%) and 67 (67.68%), in which there were 30 wild-type and 57 mutated strains in gastric tissue and 22 wild-type and 45 mutated strains in saliva. Genotype analysis showed that three-points mixed mutations were quite common, but different resistant strains were present in gastric mucosa and saliva. Compared to the high sensitivity shown by nested-ASP-PCR, the positive detection of bacterial culture with gastric tissue samples was 50 cases, in which only 26 drug-resistant strains were found through analyzing minimum inhibitory zone of clarithromycin.
Conclusion: The nested-ASP-PCR assay showed higher detection sensitivity than ASP-PCR and drug sensitivity testing, which could be performed to evaluate clarithromycin resistance of H. pylori.
Keywords: Clarithromycin resistance; Drug sensitivity testing; Helicobacter pylori; Nested-allele specific primer-polymerase chain reaction; Rapid urease test.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modified allele-specific primer-polymerase chain reaction method for analysis of susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori strains to clarithromycin.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Nov;22(11):1810-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.04919.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17914955
-
Improved allele-specific PCR assays for detection of clarithromycin and fluoroquinolone resistant of Helicobacter pylori in gastric biopsies: identification of N87I mutation in GyrA.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015 Apr;81(4):251-5. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2014.12.003. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25600075 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of mutations of the 23S rRNA gene of Helicobacter pylori by allele specific primer-polymerase chain reaction method.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Jul;22(7):1057-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04546.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17608851
-
[Development and clinical application of invader assay--detection of resistant mutation to clarithromycin in Helicobacter pylori].Rinsho Byori. 2006 Feb;54(2):176-83. Rinsho Byori. 2006. PMID: 16548239 Review. Japanese.
-
Detection of clarithromycin-resistant Helicobacter pylori by stool PCR in children: a comprehensive review of literature.Helicobacter. 2013 Apr;18(2):89-101. doi: 10.1111/hel.12016. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Helicobacter. 2013. PMID: 23067446 Review.
Cited by
-
Seven Days of Bismuth-Based Quadruple Therapy Is as Effective for the First-Line Treatment of Clarithromycin-Resistant Confirmed Helicobacter pylori Infection as 14 Days of Bismuth-Based Quadruple Therapy.J Clin Med. 2022 Jul 30;11(15):4440. doi: 10.3390/jcm11154440. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35956057 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection and antibiotic resistance - from biology to clinical implications.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Sep;18(9):613-629. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00449-x. Epub 2021 May 17. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34002081 Review.
-
Comparative analysis of the detection of antibiotic genotypic resistance with gastric mucosa, gastric fluid, and fecal samples in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection.J Clin Microbiol. 2025 Jan 31;63(1):e0103424. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01034-24. Epub 2024 Dec 16. J Clin Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39679670 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplex PCR-Mass Spectrometry Mini-Sequencing Technology Detected Antibiotic Resistance of Helicobacter pylori to Six Antibiotics.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 14;26(4):1632. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041632. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakamura A, Furuta T, Shirai N, Sugimoto M, Kajimura M, Soya Y, Hishida A. Determination of mutations of the 23S rRNA gene of Helicobacter pylori by allele specific primer-polymerase chain reaction method. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:1057–1063. - PubMed
-
- Schmitt BH, Regner M, Mangold KA, Thomson RB, Kaul KL. PCR detection of clarithromycin-susceptible and -resistant Helicobacter pylori from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded gastric biopsies. Mod Pathol. 2013;26:1222–1227. - PubMed
-
- Furuta T, Shirai N, Takashima M, Xiao F, Hanai H, Sugimura H, Ohashi K, Ishizaki T, Kaneko E. Effect of genotypic differences in CYP2C19 on cure rates for Helicobacter pylori infection by triple therapy with a proton pump inhibitor, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001;69:158–168. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

