Effects of High-Pressure, Microbial Transglutaminase and Glucono-δ-Lactone on the Aggregation Properties of Skim Milk
- PMID: 27433104
- PMCID: PMC4942548
- DOI: 10.5851/kosfa.2016.36.3.335
Effects of High-Pressure, Microbial Transglutaminase and Glucono-δ-Lactone on the Aggregation Properties of Skim Milk
Abstract
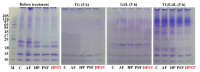
The object in this study is to investigate the effects of high pressure and freezing processes on the curdling of skim milk depending on the presence of transglutaminase (TGase) and glucono-δ-lactone (GdL). Skim milk was treated with atmospheric freezing (AF), high pressure (HP), pressure-shift freezing (PSF) and high pressure sub-zero temperature (HPST) processing conditions. After freezing and pressure processing, these processed milk samples were treated with curdling agents, such as TGase and GdL. Pressurized samples (HP, PSF and HPST) had lower lightness than that of the control. In particular, PSF had the lowest lightness (p<0.05). Likewise, the PSF proteins were the most insoluble regardless of whether they were activated by TGase and GdL, indicating the highest rate of protein aggregation (p<0.05). Furthermore, the TGase/GdL reaction resulted in thick bands corresponding to masses larger than 69 kDa, indicating curdling. Casein bands were the weakest in PSF-treated milk, revealing that casein was prone to protein aggregation. PSF also had the highest G' value among all treatments after activation by TGase, implying that PSF formed the hardest curd. However, adding GdL decreased the G' values of the samples except HPST-treated samples. Synthetically, the PSF process was advantageous for curdling of skim milk.
Keywords: aggregation; curdling; high pressure; skim milk; transglutaminase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rheological properties of milk gels formed by a combination of rennet and glucono-delta-lactone.J Dairy Res. 2000 Aug;67(3):415-27. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900004246. J Dairy Res. 2000. PMID: 11037237
-
Manufacture of acid gels from skim milk using high-pressure homogenization.J Dairy Sci. 2008 Oct;91(10):3761-7. doi: 10.3168/jds.2008-1321. J Dairy Sci. 2008. PMID: 18832197
-
Structural dependence of concentrated skim milk curd on micellar restructuring.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 3;10(1):e24046. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24046. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38230241 Free PMC article.
-
Partial calcium depletion during membrane filtration affects gelation of reconstituted milk protein concentrates.J Dairy Sci. 2015 Dec;98(12):8454-63. doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-9856. Epub 2015 Oct 9. J Dairy Sci. 2015. PMID: 26454287
-
High pressure-low temperature processing of food proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Mar;1764(3):599-618. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2005.12.009. Epub 2006 Jan 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16458618 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure on Technical Functional Properties of Edible Insect Protein.Food Sci Anim Resour. 2021 Mar;41(2):185-195. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2020.e85. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2021. PMID: 33987542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adapa S., Schmidt K. A., Toledo R. Functional properties of skim milk processed with continuous high pressure throttling. J. Dairy Sci. 1997;80:1941–1948. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(97)76135-6. - DOI
-
- Anema S. G. Effect of temperature and rate of acidification on the rheological properties of acid skim milk gels. J. Food Proc. Preserv. 2008;32:1016–1033. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4549.2008.00230.x. - DOI
-
- Anema S. G., Lauber S., Lee S. K., Henle T., Klostermeyer H. Rheological properties of acid gels prepared from pressure and transglutaminase-treated skim milk. Food Hydrocolloids. 2005;19:879–887. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2004.12.001. - DOI
-
- Arias M., Lopez-Fandiño R., Olano A. Influence of pH on the effects of high pressure on milk proteins. Milchwissenschaft. 2000;55:191–194.
-
- Balny C., Hayashi R., Heremans K., Masson P. High pressure and biotechnology: Pressure denaturation of proteins. John Libbey Eurotext; London, UK: 1992. pp. 89–99.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

