Role of bile acids in the regulation of the metabolic pathways
- PMID: 27433295
- PMCID: PMC4937164
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i13.260
Role of bile acids in the regulation of the metabolic pathways
Abstract
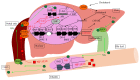
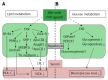
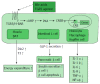
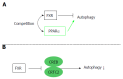
Recent studies have revealed that bile acids (BAs) are not only facilitators of dietary lipid absorption but also important signaling molecules exerting multiple physiological functions. Some major signaling pathways involving the nuclear BAs receptor farnesoid X receptor and the G protein-coupled BAs receptor TGR5/M-BAR have been identified to be the targets of BAs. BAs regulate their own homeostasis via signaling pathways. BAs also affect diverse metabolic pathways including glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism and energy expenditure. This paper suggests the mechanism of controlling metabolism via BA signaling and demonstrates that BA signaling is an attractive therapeutic target of the metabolic syndrome.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; Bile acid binding resin; Bile acids; Energy metabolism; Farnesoid X receptor; Glucose metabolism; Incretin; Lipid metabolism; Microbiota; TGR5/M-BAR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developments in understanding bile acid metabolism.Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Jan;8(1):59-69. doi: 10.1586/eem.12.75. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 30731653
-
The Role of Bile Acids in Glucose Metabolism and Their Relation with Diabetes.Ann Hepatol. 2017 Nov;16 Suppl 1:S15-S20. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.5494. Ann Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 31196630
-
Role of bile acids in overweight and obese children and adolescents.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 30;13:1011994. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1011994. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36531484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bile acids induce energy expenditure by promoting intracellular thyroid hormone activation.Nature. 2006 Jan 26;439(7075):484-9. doi: 10.1038/nature04330. Epub 2006 Jan 8. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16400329
-
Endocrine functions of bile acids.EMBO J. 2006 Apr 5;25(7):1419-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601049. Epub 2006 Mar 16. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16541101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targets and Effective Constituents of ZhiziBaipi Decoction for Treating Damp-Heat Jaundice Syndrome Based on Chinmedomics Coupled with UPLC-MS/MS.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 5;13:857361. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.857361. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35450037 Free PMC article.
-
Associations among dietary non-fiber carbohydrate, ruminal microbiota and epithelium G-protein-coupled receptor, and histone deacetylase regulations in goats.Microbiome. 2017 Sep 19;5(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s40168-017-0341-z. Microbiome. 2017. PMID: 28927467 Free PMC article.
-
The Oral-Gut Microbiota Axis Across the Lifespan: New Insights on a Forgotten Interaction.Nutrients. 2025 Aug 1;17(15):2538. doi: 10.3390/nu17152538. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40806122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular hepatitis B virus increases hepatic cholesterol deposition in alcoholic fatty liver via hepatitis B core protein.J Lipid Res. 2018 Jan;59(1):58-68. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M079533. Epub 2017 Nov 13. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 29133292 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk Between Bile Acids and Intestinal Epithelium: Multidimensional Roles of Farnesoid X Receptor and Takeda G Protein Receptor 5.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 29;26(9):4240. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094240. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Urizar NL, Dowhan DH, Moore DD. The farnesoid X-activated receptor mediates bile acid activation of phospholipid transfer protein gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:39313–39317. - PubMed
-
- Maruyama T, Miyamoto Y, Nakamura T, Tamai Y, Okada H, Sugiyama E, Nakamura T, Itadani H, Tanaka K. Identification of membrane-type receptor for bile acids (M-BAR) Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;298:714–719. - PubMed
-
- Makishima M, Okamoto AY, Repa JJ, Tu H, Learned RM, Luk A, Hull MV, Lustig KD, Mangelsdorf DJ, Shan B. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science. 1999;284:1362–1365. - PubMed
-
- Parks DJ, Blanchard SG, Bledsoe RK, Chandra G, Consler TG, Kliewer SA, Stimmel JB, Willson TM, Zavacki AM, Moore DD, et al. Bile acids: natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science. 1999;284:1365–1368. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

