Diclofenac, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, is an antagonist of human TRPM3 isoforms
- PMID: 27433342
- PMCID: PMC4876142
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.232
Diclofenac, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, is an antagonist of human TRPM3 isoforms
Abstract
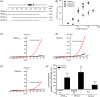
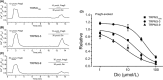
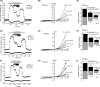
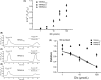
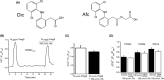
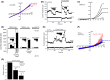
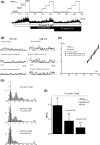
The effects of diclofenac (Dic), an acetic acid derivative-type nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, were examined on the function of transient receptor potential (TRP) melastatin (TRPM) 3 (TRPM3) in human embryonic kidney 293 cell-line (HEK293) cells with recombinant human TRPM3 isoforms (TRPM31325, TRPM3-3, TRPM3-9, and TRPM3-S) and in a neuroblastoma cell line human neuroblastoma IMR-32 cells (IMR-32 cells) derived from human peripheral neurons. TRPM3 responses evoked by pregnenolone sulfate (PregS) were effectively inhibited by Dic in a concentration-dependent manner in Ca(2+) measurement and electrophysiological assays. The apparent IC 50 for PregS-induced Ca(2+) response of TRPM31325, TRPM3-3, and TRPM3-9 was calculated to be 18.8, 42.5, and 7.1 μmol/L, respectively. The TRPM3-dependent Ca(2+) responses evoked by nifedipine, another TRPM3 agonist, were also significantly inhibited by Dic. In contrast, aceclofenac, an acetoxymethyl analog of Dic, had no effects on PregS-induced TRPM3 responses. Constitutive channel activity of TRPM3-S without TRPM3 agonists was substantially inhibited by Dic, ruling out the possibility of interaction of Dic against TRPM3 agonists to the channel binding sites. Moreover, Dic reversibly inhibited TRPM3 single-channel activity recorded in excised outside-out patches without affecting the channel conductance. In differentiated neuronal IMR-32 cells with endogenous TRPM3, Dic inhibited PregS-evoked Ca(2+) responses with an apparent IC 50 of 17.1 μmol/L. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that Dic inhibits human TRPM3 without interacting with the channel pore.
Keywords: Diclofenac; TRPM3; neuroblastoma; pain.
Figures

References
-
- Alves DP, Tatsuo MA, Leite R, Duarte ID (2004). Diclofenac‐induced peripheral antinociception is associated with ATP‐sensitive K+ channels activation. Life Sci 74: 2577–2591. - PubMed
-
- Bort R, Ponsoda X, Jover R, Gomez‐Lechon MJ, Castell JV (1999). Diclofenac toxicity to hepatocytes: a role for drug metabolism in cell toxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288: 65–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

