The Prognostic Impact of Molecular Subtypes and Very Young Age on Breast Conserving Surgery in Early Stage Breast Cancer
- PMID: 27433412
- PMCID: PMC4938212
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.633
The Prognostic Impact of Molecular Subtypes and Very Young Age on Breast Conserving Surgery in Early Stage Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Premenopausal breast cancer with a triple-negative phenotype (TNBC) has been associated with inferior locoregional recurrence free survival (LRFS) and overall survival (OS) after breast conserving surgery (BCS). The aim of this study is to analyze the association between age, subtype, and surgical treatment on survival in young women (≤40 years) with early breast cancer in a population with a high rate of breast cancer in young women.
Methods: Three hundred thirty-two patients ≤40 years old with stage I-II invasive breast cancer who underwent surgery at a single institution between 1998 and 2012 were identified retrospectively. Uni- and multivariate analysis evaluated predictors of LRFS, OS, and disease free survival (DFS).
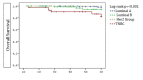
Results: Most patients (64.2%) underwent BCS. Mean age and follow-up time were 35 (25 ± 3.61) years, and 72 months (range, 24-252), respectively. In multivariate analysis, multicentricity/multifocality and young age (<35 years) independently predicted for poorer DFS and OS. Those aged 35-40 years had higher LRFS and DFS than those <35 in the mastectomy group (p=0.007 and p=0.039, respectively). Patients with TNBC had lower OS compared with patients with luminal A subtype (p=0.042), and those who underwent BCS had higher OS than patients after mastectomy (p=0.015).
Conclusion: Young age (< 35 years) is an independent predictor of poorer OS and DFS as compared with ages 35-40, even in countries with a lower average age of breast cancer presentation. In addition, TNBC in the young predicts for poorer OS. BCS can be performed in young patients with TNBC, despite their poorer overall survival.
Keywords: breast cancer; breast conserving surgery; molecular subtypes; survival; young age.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Prognoses of Young Women With Breast Cancer (≤35 years) With Different Surgical Options: A Propensity Score Matching Retrospective Cohort Study.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 28;12:795023. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.795023. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35296009 Free PMC article.
-
The different outcomes between breast-conserving surgery and mastectomy in triple-negative breast cancer: a population-based study from the SEER 18 database.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 17;8(3):4773-4780. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13976. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27999201 Free PMC article.
-
Local Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Is Mastectomy Superior to Breast-Conserving Surgery?J Pers Med. 2023 May 21;13(5):865. doi: 10.3390/jpm13050865. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37241035 Free PMC article.
-
Overall survival according to type of surgery in young (≤40 years) early breast cancer patients: A systematic meta-analysis comparing breast-conserving surgery versus mastectomy.Breast. 2015 Jun;24(3):175-81. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Breast. 2015. PMID: 25728282 Review.
-
Breast cancer under age 40: a different approach.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2015 Apr;16(4):16. doi: 10.1007/s11864-015-0334-8. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25796377 Review.
Cited by
-
Age Under 30 Years As a Predictor of Poor Survival in a Cohort of Mexican Women With Breast Cancer.Cancer Control. 2021 Jan-Dec;28:10732748211047408. doi: 10.1177/10732748211047408. Cancer Control. 2021. PMID: 34670417 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of clinicopathological factors on prognosis of young patients with resected breast cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Feb 5;100(5):e23693. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023693. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33592828 Free PMC article.
-
BREAST CANCER IN YOUNG WOMEN: PATHOLOGIC AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL FEATURES.Acta Clin Croat. 2018 Sep;57(3):497-502. doi: 10.20471/acc.2018.57.03.13. Acta Clin Croat. 2018. PMID: 31168183 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic parameters of luminal A and luminal B intrinsic breast cancer subtypes of Pakistani patients.World J Surg Oncol. 2018 Jan 2;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1299-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29291744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray FI, Devesa SS. Eur J Cancer. Vol. 37. Cancer; 2001. Cancer burden in the year 2000. The global picture; pp. 4–66. - PubMed
-
- Vahit Ozmen. Breast. Istanbul-Turkey: Yelken Basim Yayin Sanayi ve Ticaret Limited; 2013. Breast Cancer in Turkey.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources