Effects of a Comprehensive, Intensive Lifestyle Intervention Combined with Metformin Extended Release in Obese Adolescents
- PMID: 27433488
- PMCID: PMC4897295
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/659410
Effects of a Comprehensive, Intensive Lifestyle Intervention Combined with Metformin Extended Release in Obese Adolescents
Abstract
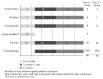
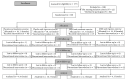
Objective. To assess a comprehensive, intensive lifestyle intervention in combination with metformin extended release (MXR) or placebo on body mass index (BMI) and risk factors for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease in obese adolescents. Study Design. Sixty-nineobese adolescents (mean BMI 32.5) received a comprehensive lifestyle intervention with structured dietary, physical activity, and behavioral components for 24 months. Subjects were randomized to 1 of 4 groups: MXR (33) 2,000 mg daily or placebo, with either moderate or vigorous intensity exercise for the first 3 months. Subsequently the exercise intervention was the same for all 4 groups. Results. Anthropometry measurements did not differ with initial exercise intensity at any time. At 3 months % body fat decreased in all 4 groups (P < 0.006). BMI and % body fat decreased in the MXR groups, but not the placebo groups, at 6 (-0.88, -3.16) and 12 months (-0.56, -2.34) (P < 0.05). Insulin resistance, fasting blood glucose, and leptin improved in all groups at 6 and 12 months. A high subject attrition rate (58%) occurred by 24 months. Conclusion. A comprehensive, intensive lifestyle intervention combined with MXR led to a decline in BMI and % body fat at 1 year independent of initial exercise intensity. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00934570 .
Figures
References
-
- Shields M. Overweight and obesity among children and youth. Health Reports. 2006;17(3):27–42. - PubMed
-
- Roberts K. C., Shields M., de Groh M., Aziz A., Gilbert J.-A. Overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: results from the 2009 to 2011 Canadian health measures survey. Health Reports. 2012;3:37–41. - PubMed
-
- Sandhu N., Witmans M. B., Lemay J.-F., Crawford S., Jadavji N., Pacaud D. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2008;21(7):631–640. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical