Human Tick-Borne Encephalitis and Characterization of Virus from Biting Tick
- PMID: 27434395
- PMCID: PMC4982194
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2208.151962
Human Tick-Borne Encephalitis and Characterization of Virus from Biting Tick
Abstract
We report a case of human tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) in which the TBE virus was isolated from the biting tick. Viral growth and sequence were characterized and compared with those of a reference strain. Virus isolation from ticks from patients with TBE may offer a new approach for studies of epidemiology and pathogenicity.
Keywords: RNA; case report; cell culture; flavivirus; sequence analysis; tick-borne encephalitis; tick-borne encephalitis virus; vector-borne infections; viruses.
Figures
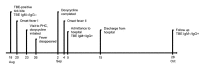
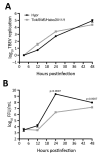
Comment in
-
Human Tick-Borne Encephalitis, the Netherlands.Emerg Infect Dis. 2017 Jan;23(1):169. doi: 10.3201/eid2301.161405. Epub 2017 Jan 15. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 27938522 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Vaccines against tick-borne encephalitis: WHO position paper. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2011;86:241–56. - PubMed
-
- Puchhammer-Stöckl E, Kunz C, Mandl CW, Heinz FX. Identification of tick-borne encephalitis virus ribonucleic acid in tick suspensions and in clinical specimens by a reverse-transcription-nested polymerase chain reaction assay. Clin Diagn Virol. 1995;4:321–6. 10.1016/0928-0197(95)00022-4 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

